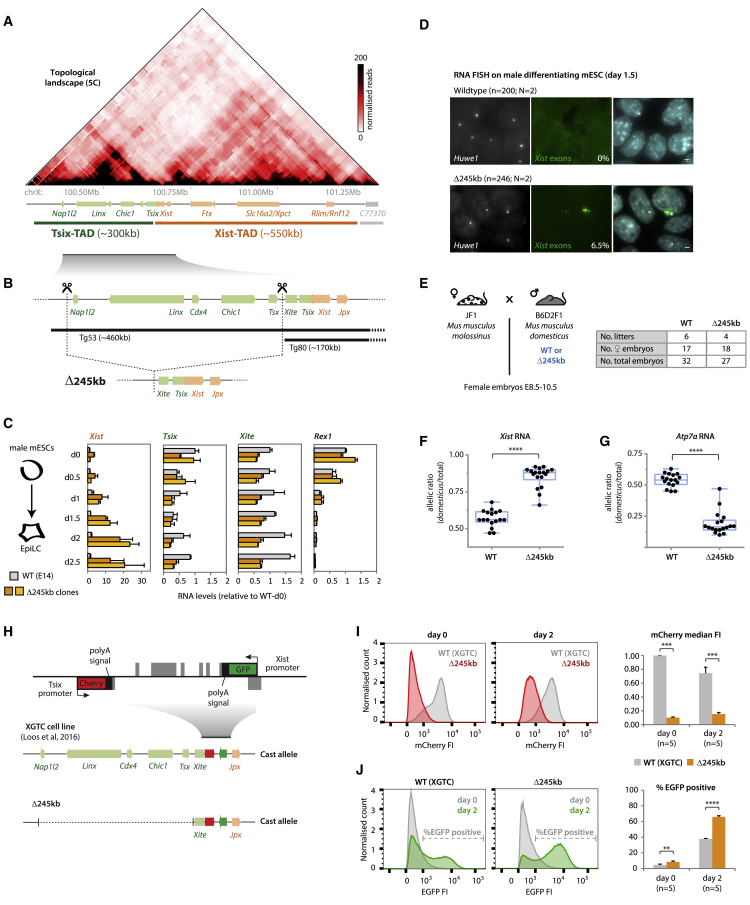
Figure 1.
The Tsix-TAD Harbors Important Elements for Both Tsix and Xist Regulation
(A) Topological organization of the Xic; the Xist/Tsix locus lies at the boundary between two TADs.
(B) Targeting strategy for deleting the ∼245-kb region included in the transgene Tg53, but not in Tg80 (Heard et al., 1999). Tg53, but not Tg80, expresses Tsix in the inner cell mass of mouse blastocysts (Nora et al., 2012); both transgenes include the Xite element.
(C) Gene expression analysis during differentiation. Data are normalized to wild-type day 0 for each gene, and represents the average of two biological replicates for each genotype.
(D) RNA FISH for Huwe1 (X-linked gene) and Xist (exonic probe) on mESCs differentiated to day 1.5. Percentage of cells with Xist RNA accumulation is indicated and represents an average from two independent clones (SD = 0.07%). Scale bar, 2 μm.
(E) Cross used for analysis of RNA allelic ratios in female hybrid embryos. The table summarizes the number of embryos collected.
(F and G) RNA allelic ratios for Xist (F) and Atp7a (G), an X-linked gene. Each black dot corresponds to a single female embryo. Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann-Whitney test (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). Reverse cross shown in Figure S1F.
(H) Schematic representation of the XGTC female line (129/Cast), which harbors a double knockin on the Cast allele, with EGFP replacing Xist exon-1 and mCherry replacing Tsix exon-1. We generated Δ245 kb on the Cast allele.
(I and J) Cytometry profiles of mCherry (I) and EGFP (J) at day 0 and day 2 of differentiation. On the right, (I) median fluorescence intensity (FI) of mCherry (normalized to wild-type day 0) or (J) percentage of EGFP-positive cells, based on illustrated threshold. Wild-type data represent an average of five experimental replicates. Δ245-kb data represent an average of two independent clones, five experimental replicates for each. Statistical analysis was performed using a paired two-tailed t test (∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).