Figure 2.
The Linx Locus Harbors cis-Regulatory Elements that Control XCI Choice
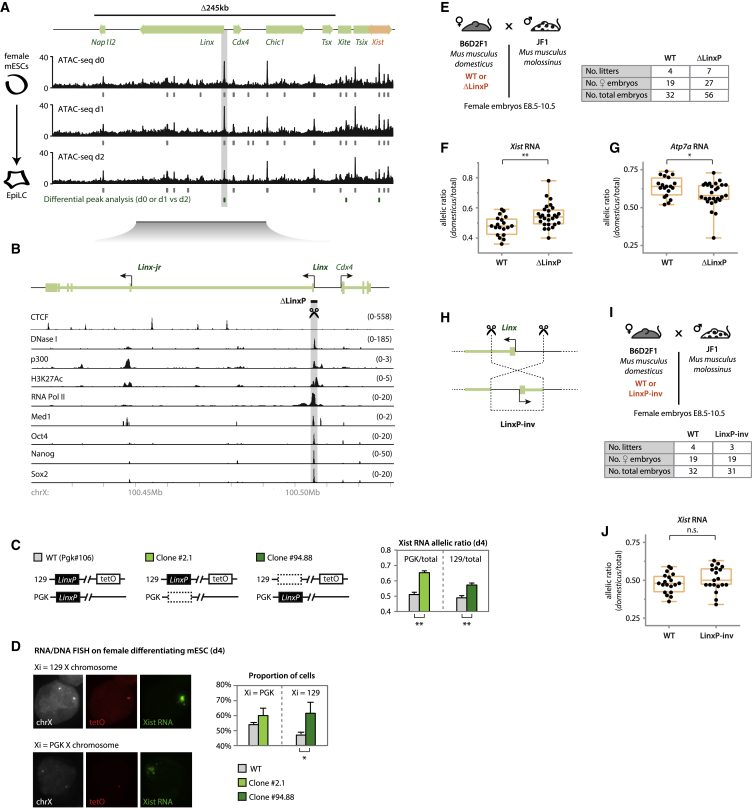
(A) ATAC-seq data for the Tsix-TAD region in differentiating XX mESCs. For each time point, results of peak calling are represented by gray marks below the data. Green marks depict differential peak analysis. Identical results were found for day 0 versus day 2 and day 1 versus day 2 (p < 0.01) within the region of interest, while no differential peaks were found for day 0 versus day 1. Gray box highlights the promoter of Linx, the only differential peak within the Δ245-kb region. Normalized data are shown for one replicate (second replicate in Figure S2A); peak analysis was performed on both replicates. See STAR Methods for more details.
(B) The Linx locus and its chromatin features (see STAR Methods for sources of datasets represented). The position of introns and exons is based on Nora et al. (2012) and mESC RNA Scripture (Guttman et al., 2010). Targeted region LinxP (∼2 kb) is indicated.
(C) Allelic quantification of Xist RNA by pyrosequencing at day 4 of differentiation. Note that each clone harbors the deletion in a different allele and Xist RNA allelic ratios are shown from one or the other allele, depending on the mutant clone that is being compared. Data are presented as means, and error bars represent SEM (six biological replicates). Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed paired t test with Bonferroni’s correction (∗∗p < 0.01).
(D) Determining which allele is more frequently coated by Xist RNA using RNA/DNA FISH. The two alleles can be distinguished due to a TetO array present on the 129 allele (Masui et al., 2011). X chromosomes are identified by using a probe for the Tsix/Xist region. Data are presented as means, and error bars represent SD (two biological replicates, more than 80 cells per genotype counted for each). Statistical analysis was performed using a chi-square test (∗p < 0.05).
(E and I) Crosses used for analysis of RNA allelic ratios in female hybrid embryos. The table summarizes the number of embryos collected.
(F and G) RNA allelic ratios for Xist (F) and Atp7a (G), an X-linked gene. Each black dot corresponds to a single female embryo. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed t test (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01). Reverse cross shown in Figure S3E.
(H) Inversion of the LinxP element.
(J) Analysis of Xist RNA allelic ratios. Each black dot represents the ratio for a single female embryo. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed t test. Analysis of Atp7a RNA allelic ratios and reverse cross is shown in Figure S3G.