Figure 1. Chromatin-associated proteins in learning and memory formation.
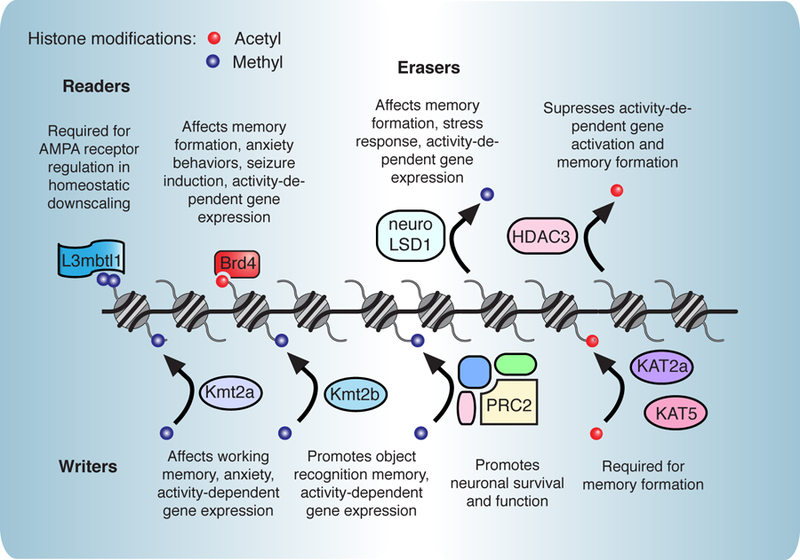
Numerous reader [4,5*,6*], writer [9,10**,11–14], and eraser [15*,16, 41] proteins have recently been implicated in neuronal function. In particular, these proteins regulate activity-dependent gene expression and key synaptic receptor genes. In addition, many have been implicated in various forms of synaptic plasticity and various types of learning and memory formation.
