Figure 3. Chromatin and enhancers co-regulate activity-dependent gene activation in neurons.
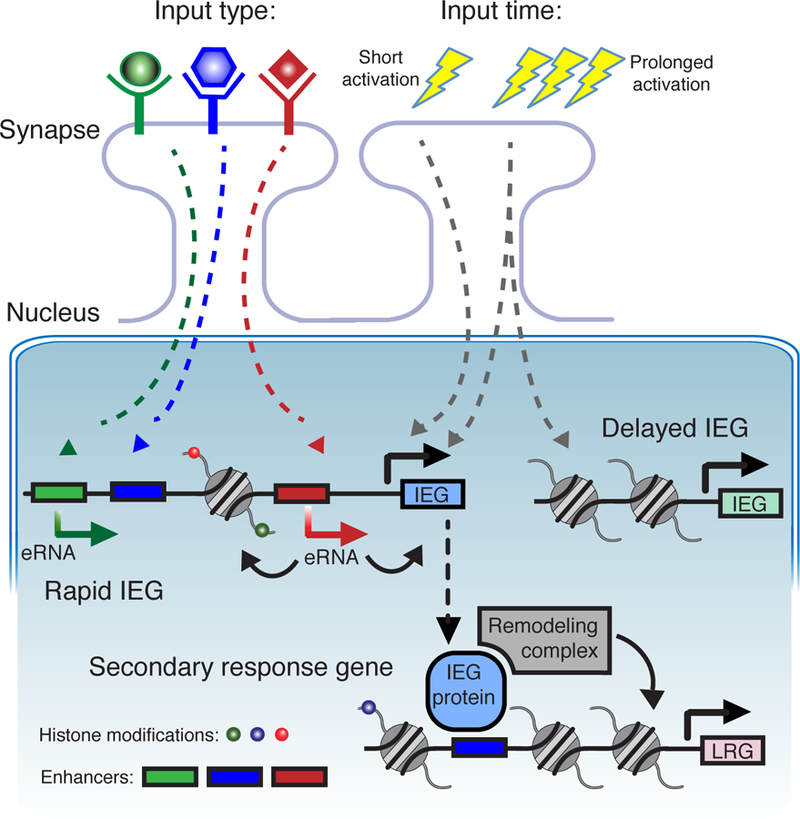
The combinatorial effects of enhancers and chromatin allow neurons to distinguish between different types of stimuli [38*] and different lengths of stimuli [39*]. Different signaling pathways activate different enhancers. This generates specific eRNAs [34] which in turn affect promoter activity and the surrounding chromatin. The most rapidly induced IEGs have more open chromatin with marks such as H3K27ac near gene promoters [34, 35]. The gene products of IEGs include transcription factors which can then regulate late response genes (LGRs) and recruit chromatin regulators and remodelers such as the BAF complex [40]. IEG, immediate early gene. eRNA, enhancer RNA.
