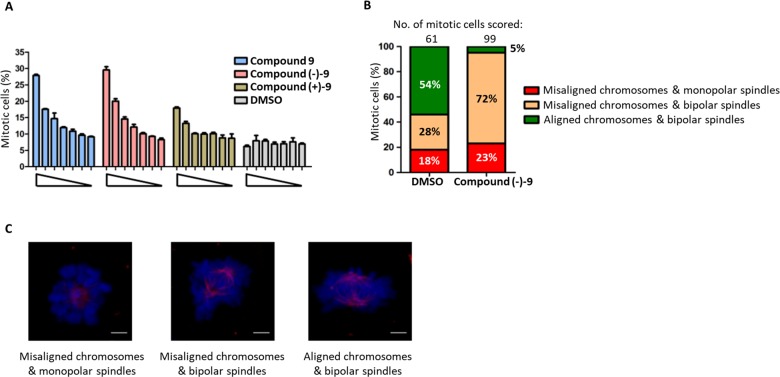
Figure 3.
Dose-dependent increase in mitotic arrest with chromosome congression defects is caused upon treatment with Compound 9 and its enantiomers. (A) Cells were treated with Compound 9 and its enantiomers, compounds (−)–9 and (+)–9 (at 200, 100, 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25, and 0 μM) and corresponding DMSO controls for 12 h. Mitotic cells scored as phospho-histone H3-stained cells per 2000 Hoechst 33342-stained nuclei in a high-content screening platform as described earlier.27 Each bar is a mean of three replicates ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The data presented is representative of two independent experiments. (B) HeLa cells were treated with compound (−)–9/DMSO for 12 h, as shown in A. The cells were fixed and stained for DNA and β-tubulin. Mitotic cells were identified by microscopy and scored under three categories: (a) misaligned chromosomes and monopolar spindles, (b) misaligned chromosomes and bipolar spindles, and (c) aligned chromosomes and bipolar spindles. The quantification of the cellular phenotype is shown in the histogram. (C) Representative maximal-intensity projection images of cells in each category (as in B) showing DNA in blue and spindle microtubules in red. The scale bar is 3 μm.