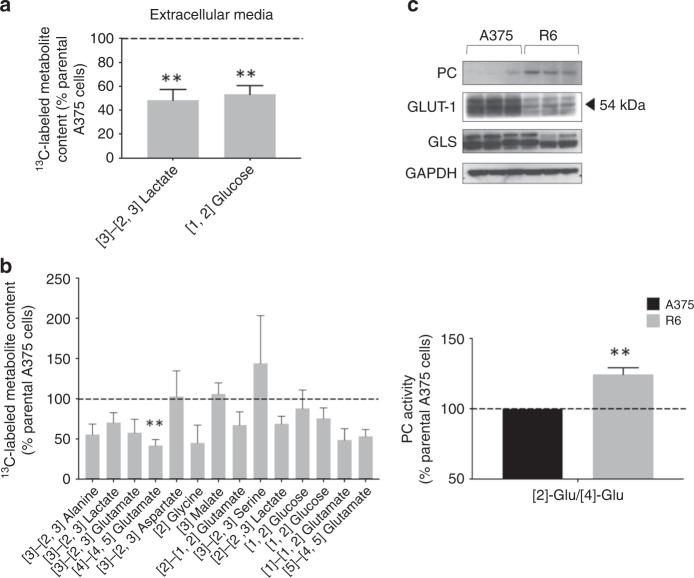
Fig. 4.
Vemurafenib-resistant cell clones exhibit decreased glycolytic metabolism and enhanced mitochondrial anaplerotic metabolism. a Resistant R6 cells produce significantly less lactateE and show a significantly lower glucose uptake in comparison to A375 cells. b R6 cells produce significantly less glutamate ([4]-[4,5] glutamate) than sensitive cells but maintain similar fumarate and acetate levels despite a lower glucose consumption rate, indicating a potential upregulation in TCA activity non-glutamine or PDH dependent. Anaplerotic TCA activity is significantly higher in R6 cells compared to the parental clone (p = 0.01). c The molecular analysis of three biological replicates from A375 and R6 cells revealed a lower GLUT-1 and GLS (KGA and GAC isoforms) expression and a higher PC expression in vemurafenib-resistant cells in comparison to sensitive cells. **p < 0.01.