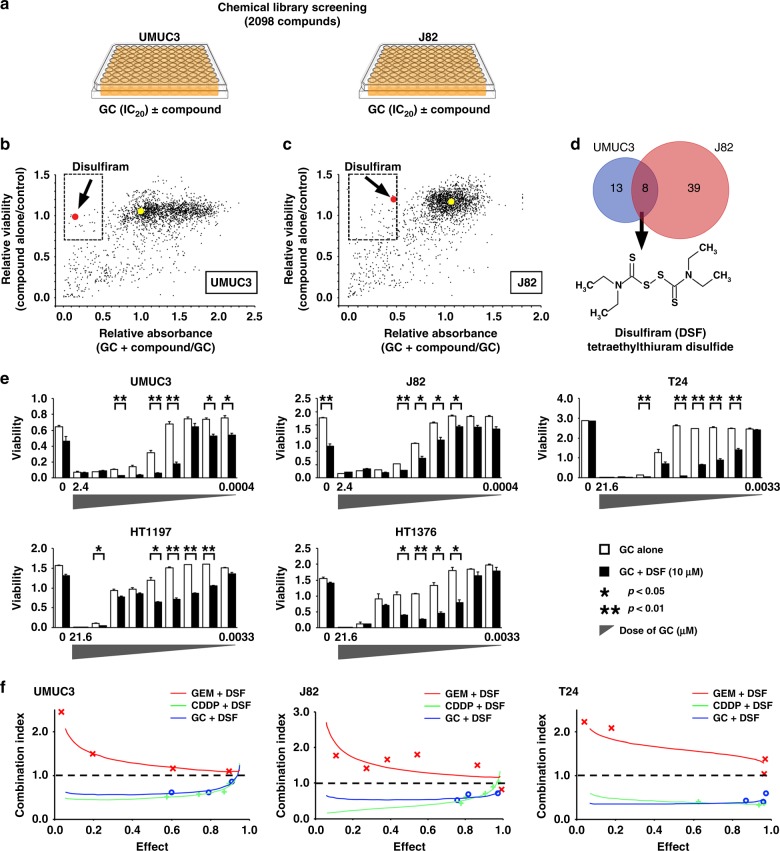
Fig. 1.
Combinatorial high-throughput screen identified DSF as a synergistic sensitiser of CDDP. a Chemical screening strategy. UMUC3 and J82 cells were treated with GC at IC20 concentrations alone or in combination with 2,098 compounds from the chemical library. After 72 h, cell viability was determined by using WST-8 assay. b, c Each compound is expandedly scattered according to the relative cell viability of treatment with compound alone to the control (water) and relative cell viability of treatment with GC plus compound to GC alone (b; UMUC3, c; J82). Hit compounds are shown in the dashed squares (compound alone/control ≥ 0.7 and GC + compound/GC ≤ 0.5). Red dots indicate DSF and yellow dots indicate vehicle. d Venn diagram showing eight compounds that sensitised both UMUC3 and J82 cells to GC in the initial screening. Further validation narrowed the compounds into the strongest sensitiser, DSF, an FDA-approved drug for alcoholism. e Enhancement of GC cytotoxicity by DSF in bladder cancer cells. Five bladder cancer cell lines were treated with 10 μM DSF, and varied concentrations of GEM (indicated on the x axis) and CDDP were fixed at a ratio of 1:100 for 72 h and evaluated by WST-8 assay. f Combination index for combined treatments of Gem plus DSF, CDDP plus DSF and GC plus DSF was determined by using CalcuSyn software. A combination index < 1 (dotted line) denotes synergy. DSF shows synergism with CDDP but not with Gem in all cell lines