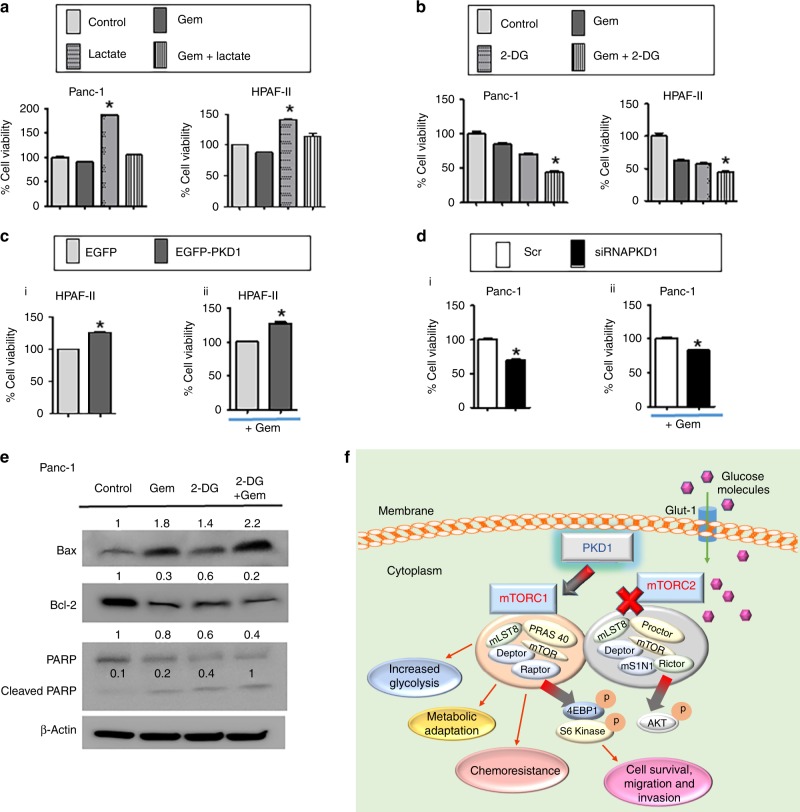
Fig. 6.
PKD1 modulation sensitises gemcitabine response in pancreatic cancer cells. a Effect of cell proliferation on treatment with gemcitabine following l-lactate and b 2DG supplementation. c i Effect of PKD1 overexpression on cell viability and c ii gemcitabine response in HPAF-II cells. d i Effect of PKD1 silencing on cell viability and d ii sensitization of gemcitabine. e Immunoblotting assay demonstrating the changes in the expression of apoptotic proteins following treatment with gemcitabine in the presence and absence of 2DG. P-values are denoted as *P < 0.05. f Schematic representation depicting the involvement of PKD1 that regulated the molecular signalling pathway that causes impaired glucose metabolism in pancreatic cancer. PKD1 acts as the main regulator of the glucose metabolic network through Glut-1 and mTORC1 activation, which in turn leads to increased metabolic adaptation in pancreatic cancer cells resulting in enhanced proliferation, invasion and chemo-resistance in pancreatic cancer cells. The blots were re-probed multiple times with β-actin being used as a protein-loading control