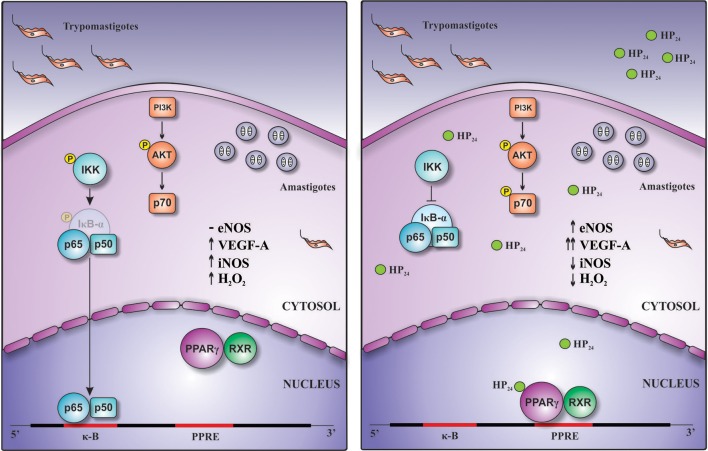
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the pro-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory actions of HP24 in T. cruzi-infected macrophages. Treatment of T. cruzi-infected macrophages with HP24 exerts pro-angiogenic effects, increasing the expression of eNOS and of VEGF-A. This effect depends on both PPARγ and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. Besides, HP24 avoids activation of NF-κB, thereby preventing iNOS expression, NO release, and H2O2 production. This anti-inflammatory effect occurs in a PPARγ-dependent manner.