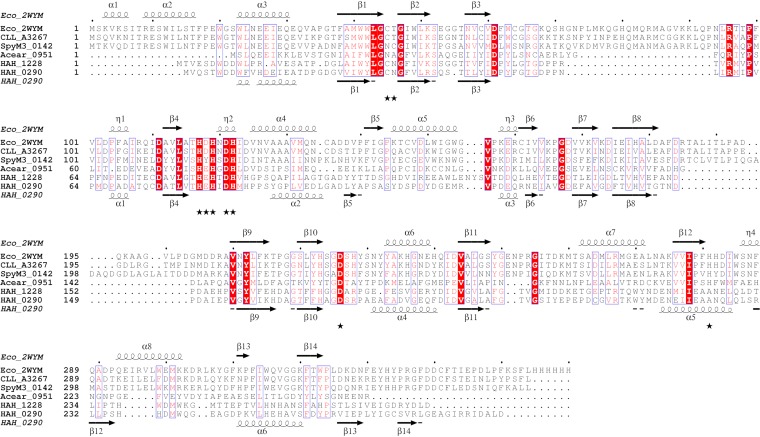
FIG 5.
Multiple-sequence alignment (calculated with ClustalX [28]) of pentonolactonase from Haloarcula hispanica, l-ascorbate 6-phosphate lactonase (UlaG) from E. coli, and UlaG homologs from other bacteria. Structure-based secondary structure elements of UlaG from E. coli and the predicted secondary structure (29) of pentonolactonase from H. hispanica are displayed using ESPript 3.0 (30). Conserved amino acid residues are indicated in red. Residues that contribute to the Mn2+ binding site of UlaG from E. coli are indicated by asterisks. Eco_2WYM (PDB identifier 2WYM), E. coli l-ascorbate 6-phosphate lactonase; CLL_A3267, Clostridium botulinum B strain Eklund 17B (NCBI accession no. YP_001887453); SpyM3_0142, Streptococcus pyogenes MGAS315 (NCBI accession no. NP_663946); Acear_0951, Acetohalobium arabaticum DSM 5501 (NCBI accession no. YP_003827546.1); HAH_0290, H. hispanica, pentonolactonase; and HAH_1228, H. hispanica, a paralog of pentonolactonase.