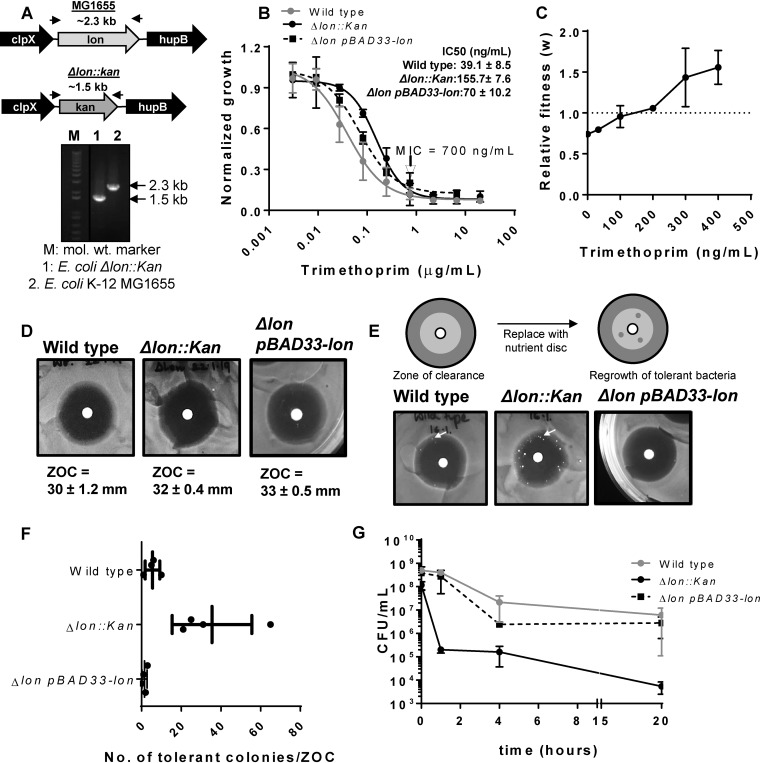
FIG 1.
Impact of Lon deficiency on intrinsic trimethoprim tolerance and resistance is contingent on drug concentration. (A) Confirmation of the Δlon::kan strain using genomic PCR. The upper panel shows the genome neighborhood of the lon gene in wild-type (MG1655) or Δlon::kan strains (not drawn to scale). Locations of primers used for PCR are indicated by arrows, and the expected amplicon sizes are also indicated. The lower panel shows the PCR confirmation of replacement of the lon gene with a kanamycin resistance cassette. mol. wt., molecular weight. (B) Trimethoprim dose-response curves for wild-type, Δlon::kan, and pBAD33-Lon-harboring E. coli Δlon::kan strains. Peak optical density after 15 to 18 h of growth at each trimethoprim concentration was normalized to growth in drug-free medium (normalized growth). Means ± standard deviations (SD) of results from 3 independent experiments are plotted. The MICs for the two strains were identical and are indicated in the graph. IC50 values (means ± standard errors of the means [SEM]) estimated from the data are provided as an inset. (C) Relative fitness (w) of E. coli Δlon::kan compared to wild-type E. coli calculated as a function of trimethoprim concentration. Fitness of the wild type is represented by a value of 1 by definition and marked with a dotted line. Means ± SD of results from 3 independent experiments are plotted. (D) Trimethoprim resistance of E. coli Δlon::kan, pBAD33-Lon rescue strain, and the wild type assessed by a disc diffusion assay. Similar diameters of zones of clearance (ZOC) were observed for the wild-type and Δlon::kan strains. Means ± SD of the diameters of the ZOC from 3 independent experiments are shown. (E) TDtest for trimethoprim tolerance for E. coli Δlon::kan, pBAD33-Lon rescue strain, and wild type. The antibiotic disc in a standard disc diffusion assay is replaced with a nutrient disc to allow growth of surviving bacteria within the ZOC (see schematic). Trimethoprim-tolerant bacteria (indicated by arrow) were more numerous for E. coli Δlon::kan than for the wild-type or plasmid rescue strain. Representative data from experiments performed at least thrice are shown. (F) Quantitation of the number of trimethoprim-tolerant colonies obtained in the ZOC from 3 or 4 independent experiments. (G) Survival of wild-type, E. coli Δlon::kan, and pBAD33-Lon rescue strains at 10 μg/ml (∼14× MIC) trimethoprim. Means ± SEM of results from 3 independent experiments are plotted.