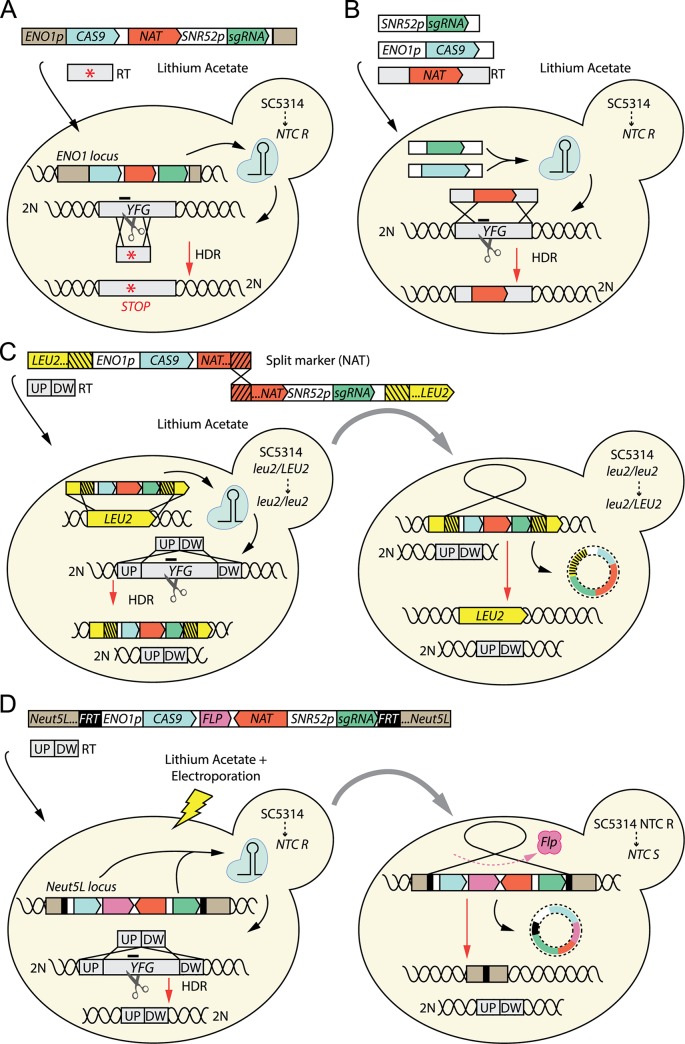
Fig 1. CRISPR–Cas9 methods in Candida albicans.
The vignettes illustrate four representative methods used for CRISPR–Cas9 genetic manipulation of C. albicans. The constructs expressing Cas9 and the sgRNA and the RT are depicted. Promoter sequences are in white, unless they constitute part of the upstream homology arm for the integration in the genomic locus, in which case they have the same color as the gene targeted for integration. The transformation method is also indicated. The targeted site on YFG is indicated by a dash. The ploidy of the alleles is indicated next to the DNA helix. (A) CAS9, the sgRNA, and the NAT cassette are stably integrated at the ENO1 locus, and HDR mediates the introduction of an RT carrying a stop codon following Cas9-induced cleavage [18]. (B) Transformation of linear DNA fragments into the cell results in transient expression of Cas9 and sgRNA, and HDR results in the integration of a NAT cassette into the targeted locus [33]. A further modification of this system allows for marker recycling [34]. (C) In the LEUpOUT approach, a split-marker strategy enables the in vivo reconstitution of the selectable cassette for the expression of the CRISPR elements. Integration of the reconstituted cassette disrupts the functional LEU2 locus of a LEU2/leu2 heterozygous strain. HDR between the targeted locus and the RT following Cas9 cut results in the deletion of the gene. HDR between directed repeats flanking the cassette (depicted as black lines on yellow background) mediates the removal of CRISPR elements and the restoration of the LEU2 ORF, which can be selected on leucine dropout medium [35]. Note that the leu2 deleted allele originally present in the LEU2/leu2 heterozygous strain remains untouched during the entire procedure, and so it is not depicted in the scheme. (D) An improved version of the method depicted in (A) allows for marker recycling. A cassette expressing the CRISPR elements and containing a FLP recombinase is flanked by FRT sequences (targets of Flp) and homology arms that mediate its integration in the Neut5L locus. HDR with an RT results in the target gene deletion. Activation of the inducible promoter driving the expression of Flp is followed by excision of the cassette, leaving only an FRT sequence in the Neut5L locus [30]. CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; DW, downstream; HDR, homology-directed repair; NTC R, Nourseothricin resistant; NTC S, Nourseothricin susceptible; ORF, open reading frame; RT, repair template; sgRNA, single-guide RNA; UP, upstream; YFG, your favorite gene.