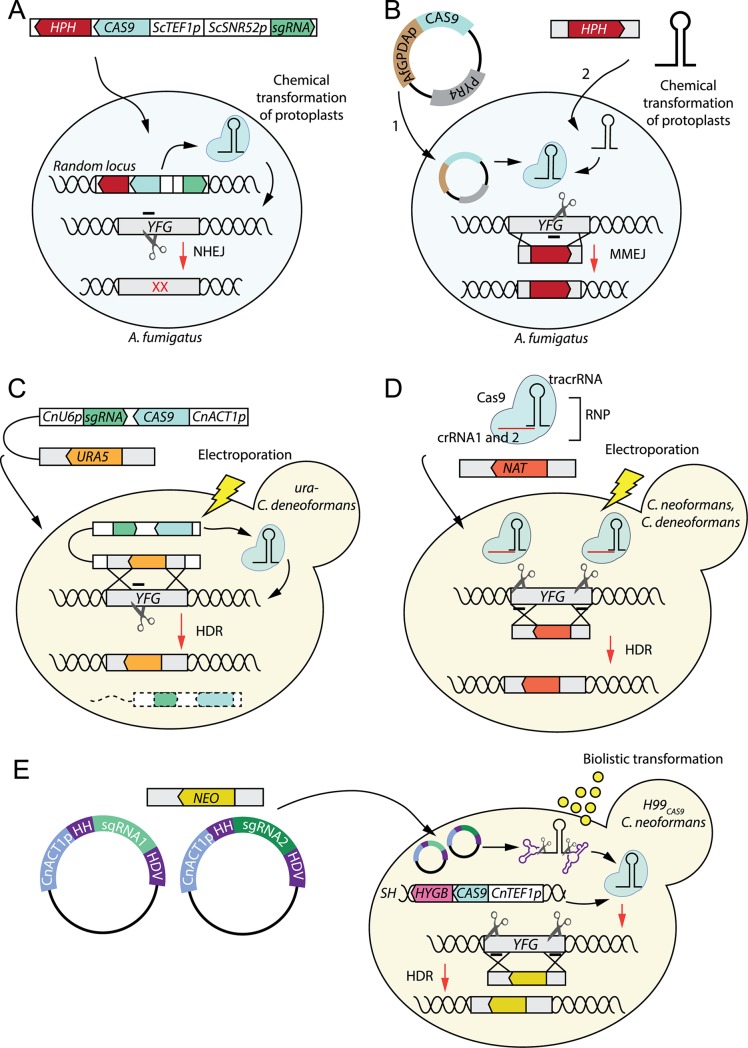
Fig 3. CRISPR–Cas9 methods in Aspergillus fumigatus, Cryptococcus neoformans and C. deneoformans.
The vignettes illustrate representative methods for CRISPR–Cas9 genetic manipulation of A. fumigatus (A–B), C. neoformans, and C. deneoformans (C–E). All the species depicted here are haploid. (A) In A. fumigatus, the CRISPR elements are integrated randomly in the genome of protoplasts and selected due to the presence of an HPH cassette. NHEJ results in indels at the cleavage site [16]. (B) MMEJ can be used to integrate an HPH cassette into a desired locus by using short homology arms. The strain is first transformed with a plasmid expressing Cas9 and containing a PYR4 marker and then with an in vitro transcribed sgRNA and the HPH cassette [45]. (C) In this “suicide” system, a cassette containing both the CRISPR elements and a URA5 marker flanked by homology arms to the target site can be transformed into an uracil auxotrophic strain of C. deneoformans. The double-strand break induced by the transiently expressed Cas9 is repaired by HDR with the URA5 cassette, and the crossover results in the release of the DNA of the CRISPR elements that induced the cleavage in the first place, which may be degraded (hence the name “suicide” system) [17]. (D) An RNP method was developed for C. neoformans and C. deneoformans, similar to the one adapted to Candida species. The cells are transformed with a mixture of two RNPs, each targeting a different end of the target gene, thus maximizing the chances of gene deletion [27]. (E) CAS9 can be integrated in the Safe Haven on C. neoformans H99 and selected due to the presence of a HYGB cassette. This strain is then be transformed with two transient plasmids expressing two sgRNAs flanked by ribozymes from the native ACT1 promoter, targeting the beginning and the end of the target gene. A NEO cassette flanked by homology arms to the target gene is used for HDR [53]. Af, Aspergillus fumigatus; Cn, Cryptococcus neoformans; CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; crRNA, CRISPR-RNA; HDR, homology-directed repair; HDV, human hepatitis delta virus; HH, hammerhead; MMEJ, microhomology-mediated end joining; NHEJ, nonhomologous end joining RNP, RNA–Cas9 protein complex; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; sgRNA, single-guide RNA; tracrRNA, trans-activating RNA; YFG, your favorite gene.