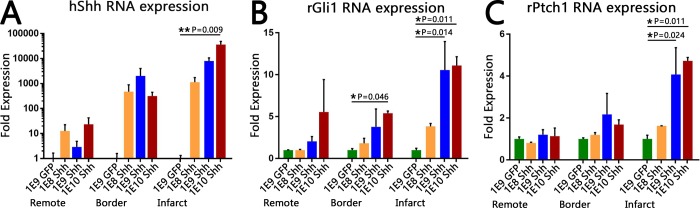
Fig 1. Injection of hShh virus increases expression of hShh RNA and induces Hh pathway activation within infarcted myocardium.
Fold expression levels of the indicated RNA within the remote uninfarcted LV, the border zone, and the infarct after injection with either 109 vp of the GFP virus, or the indicated dose of Shh virus. Error bars are SEM. n = 3 animals for GFP injection, n = 2 animals for each Shh dose. (A) Human Shh RNA expression levels, depicted on a logarithmic scale. Expression within the infarct was dose-dependent, with the highest dose inducing over 10,000 fold higher expression of hShh RNA than the GFP virus in the same region. (B, C) Rat Ptch1 (B) and rat Gli1 (C) RNA expression levels, depicted on linear scales. Both genes showed statistically significant increases in RNA expression within the infarct for the two highest doses of Shh virus.