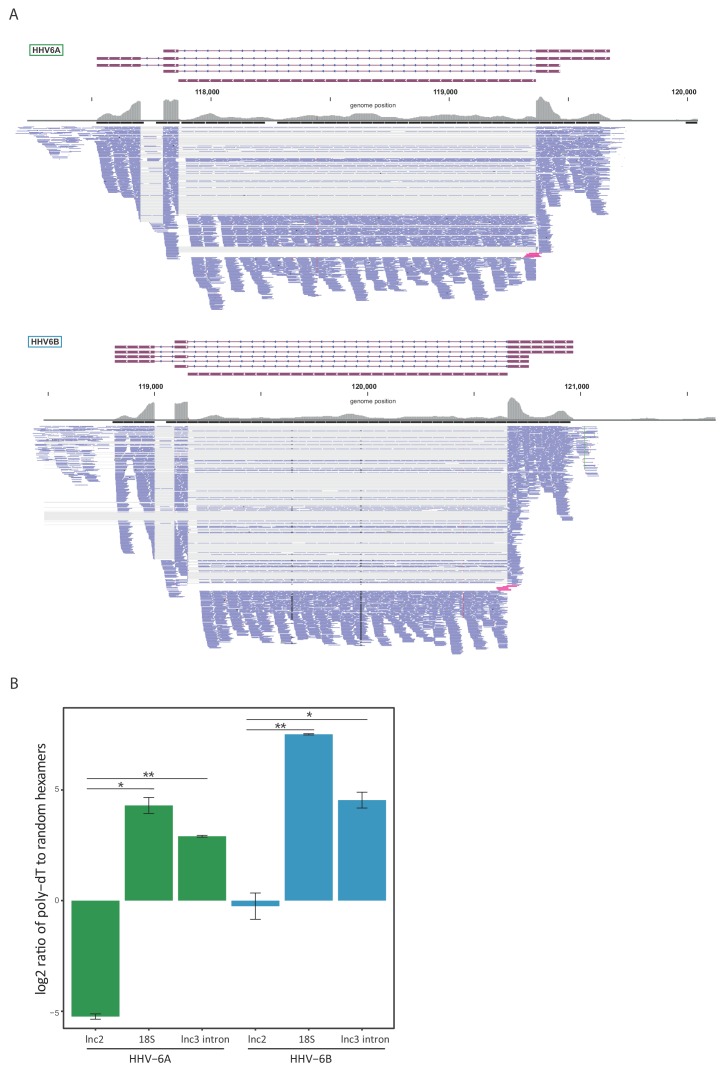
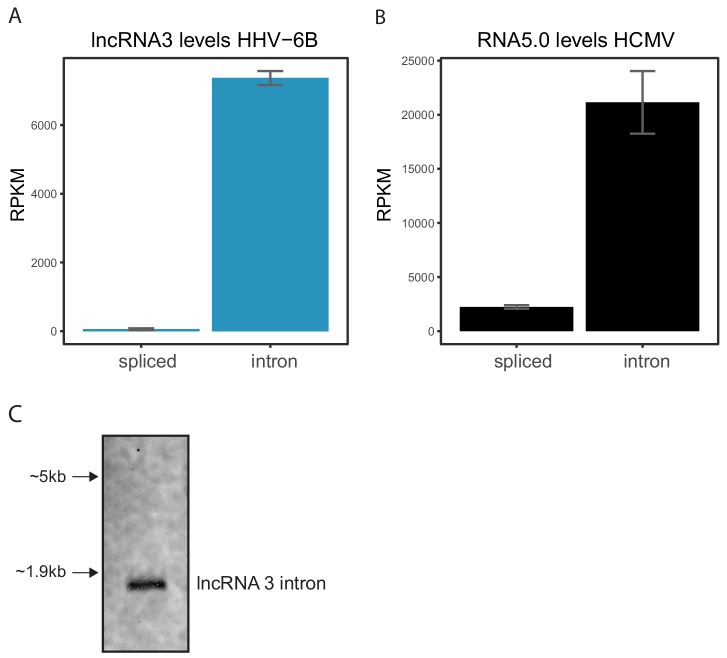
Figure 5. lncRNA3 generates a stable non poly adenylated intron.
(A) RNA-seq reads aligned to the negative strand of lncRNA3 locus in both HHV-6A and HHV-6B are presented. Thin gray lines represent spliced reads, blue lines represent reads aligned to either the exons or intron, pink lines represent reads that span the first exon intron junction. In regions with very high coverage (>100 reads per 50 nt region) reads were downsampled so that maximum 100 reads per region are displayed. Gray bars represent the total reads coverage without omissions. (B) RT-qPCR measurements of the HHV-6A and HHV-6B lncRNA3 intron RNA. Values were normalized to the HHV-6 U21 gene. cDNA was prepared with either oligo-dT or random hexamers primers and the ratio of these measurements is presented. Error bars represent standard error of biological duplicates. P-values were calculated using Student's t-test. * p-value<0.05 and ** p-value<0.01.