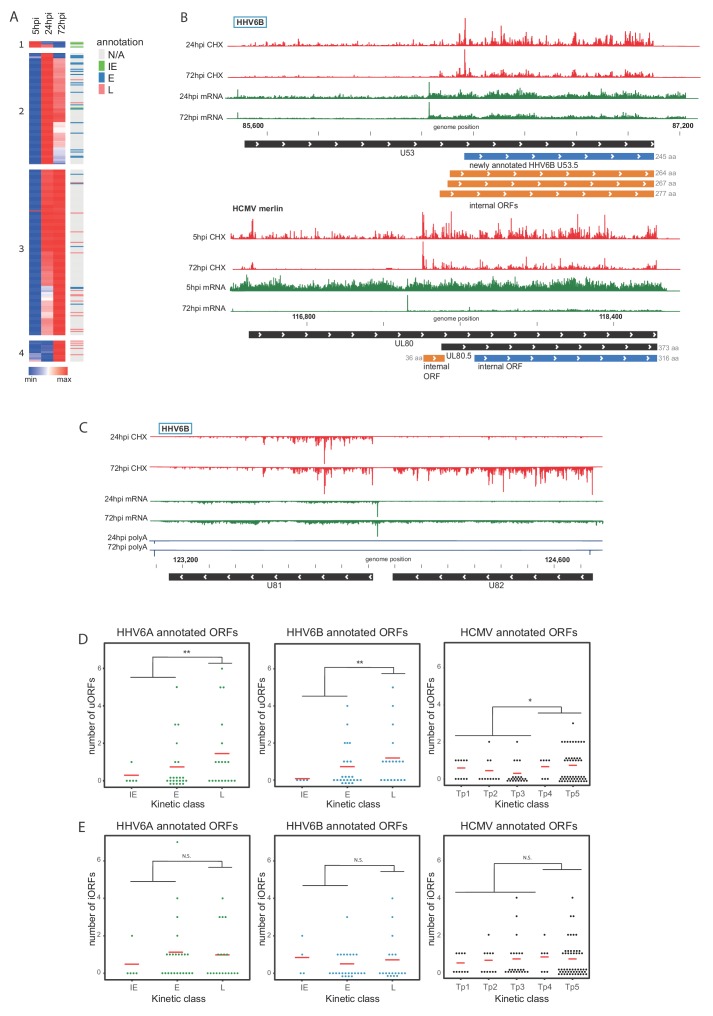
Figure 7. Temporal regulation of viral gene expression is driven by pervasive use of alternative 5’ ends.
(A) Heatmap of ribosome occupancy of HHV-6B ORFs clustered by relative expression levels at 5, 24 and 72hpi. Previously annotated kinetic class were labeled on the right as immediate early (IE, green), early (E, blue), late (L, pink), or unknown (N/A, gray). The cluster number appears on the left. (B and C) The ribosome occupancy (red) and mRNA profiles (green) are shown (B) around U53 loci at different hours post infection (marked on the left) and around its HCMV homolog, UL80 (C) and around U81 and U82 loci. (D and E) Dot plots showing the number of uORFs (D) and iORFs (E) of each canonical viral ORF with annotated kinetic class for HHV-6A, HHV-6B and HCMV. P-value was calculated using proportion test. * for p-value<0.05, ** for p-value<0.01 and N.S for non-significant.
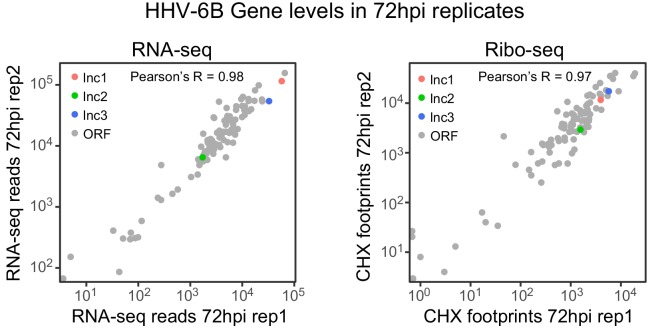
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. RNA abundance and ribosome footprint coverage correlate well between replicates.
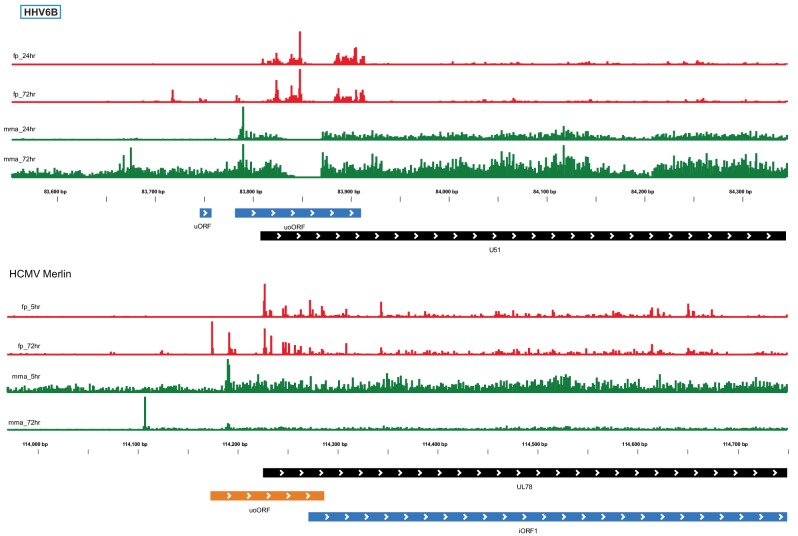
Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Conserved temporal regulation of translation from uoORF.
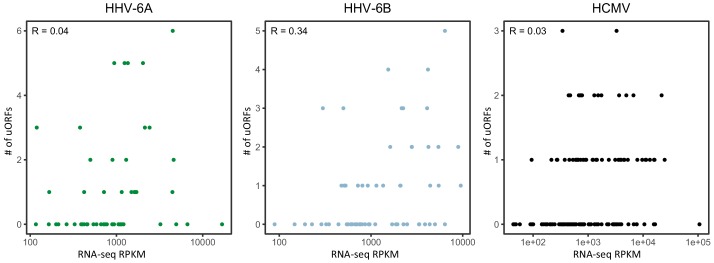
Figure 7—figure supplement 3. Number of uORFs as a function of RNA abundance.
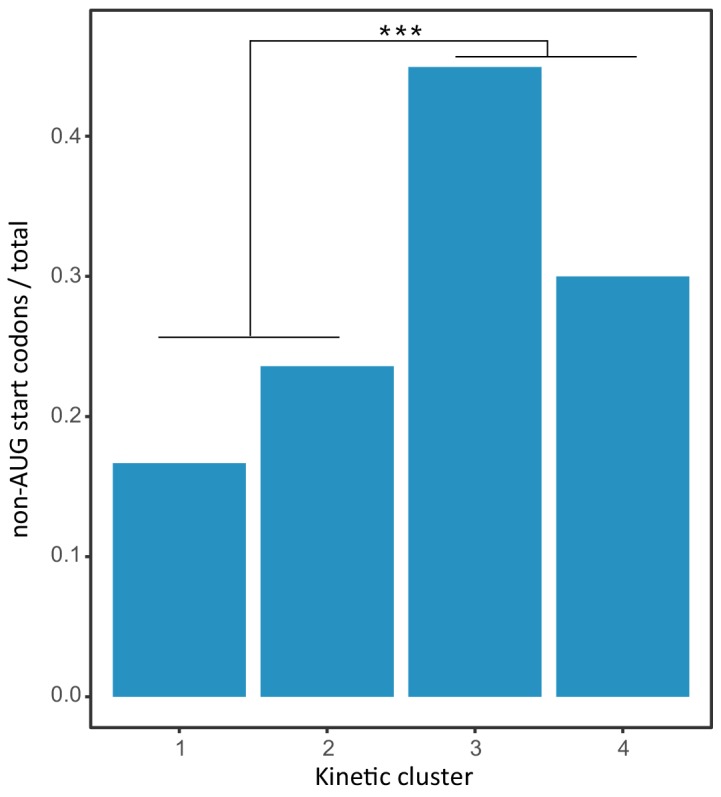
Figure 7—figure supplement 4. Enrichment of non-AUG start codons at late time points post infection.