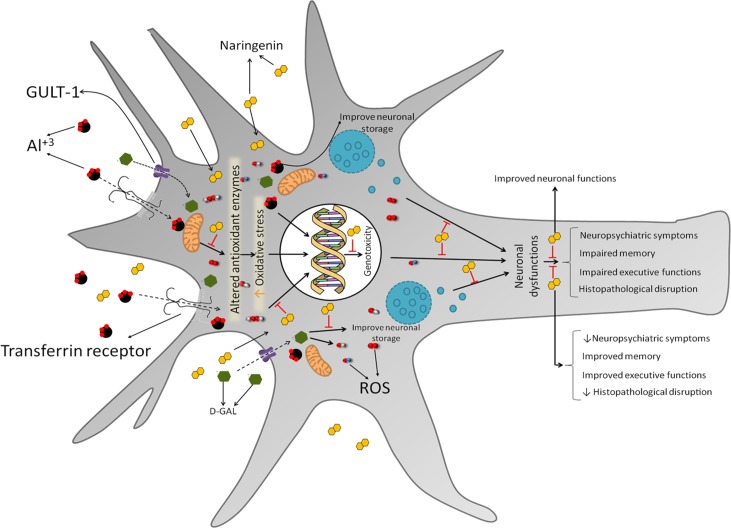
Fig 12. Schematic representation showing the possible mechanism by which naringenin protects brain against AD-like symptoms induced by co-administration of Al and D-galactose.
The findings of the present study demonstrate the antioxidant potential of NAR evident by reduced oxidative and improved activities of antioxidant enzyme activities following the administration of Al and D-galactose. This results in reduced genotoxicity and improved neuronal activity including cholinergic, serotonergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission. Pre-treatment with NAR significantly protects neurobehavioral alterations and improves cognitive, executive and psychological functions in rats. Hence, along with cognitive improvement NAR may be considered as a useful compound in the therapeutic management of behavioral disturbances associated with AD.