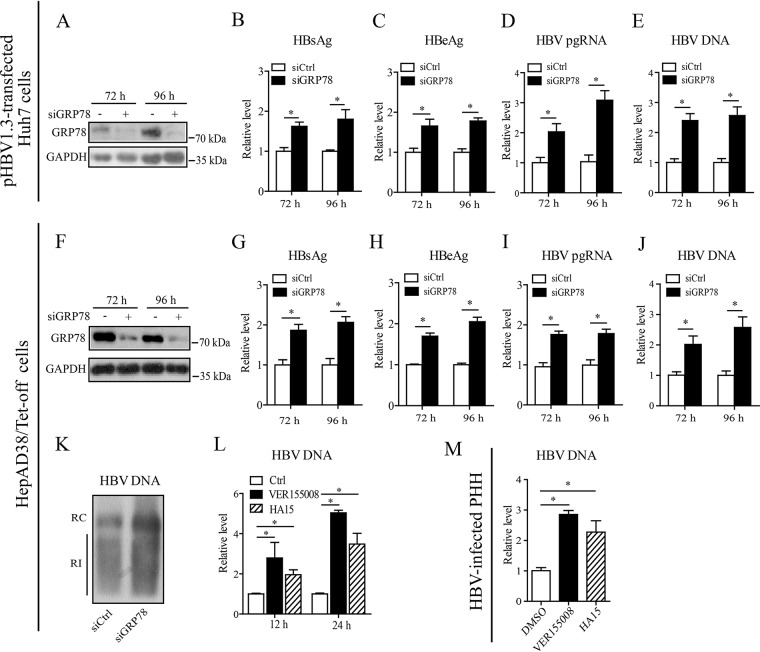
FIG 3.
Inhibition of GRP78 enhanced HBV replication. (A to E) Huh7 cells were transfected with GRP78 siRNA (siGRP78) or control siRNA (siCtrl), followed by the transfection of pHBV1.3. At 48 and 72 h posttransfection, the GRP78 expression level was examined by Western blotting (A), the levels of HBsAg (B) and HBeAg (C) were measured by ELISA, and the level of pgRNA (D) or intracellular HBV-DNA (E) was quantified by qRT-PCR or qPCR, respectively. The data are means ± the SEM of five samples pooled from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05. (F to J) HepAD38/Tet-off cells were electrotransfected with siGRP78 or siCtrl. At 72 and 96 h posttransfection, the HepAD38 cells were harvested. The levels of GRP78 protein (F), HBsAg (G), HBeAg (H), pgRNA (I), and HBV DNA (J) were determined as in panels A to E. The data are means ± the SEM of four samples pooled from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05. (K) HepAD38 cells were treated as in panels F to J. HBV replicative intermediates were detected by Southern blotting. (L) HepAD38 cells were treated with VER155008 (20 μM) or HA15 (10 μM) for 12 or 24 h, and the intracellular HBV DNA was then extracted and subjected to quantification by qPCR. The data are means ± the SEM of four samples pooled from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05. (M) PHHs were infected with HBV as in Fig. 1D. At day 7 postinfection, the cells were treated with VER155008 (20 μM) or HA15 (10 μM) for 24 h, and the HBV DNA level was determined by qPCR. The data are means ± the SEM of three samples pooled from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05.