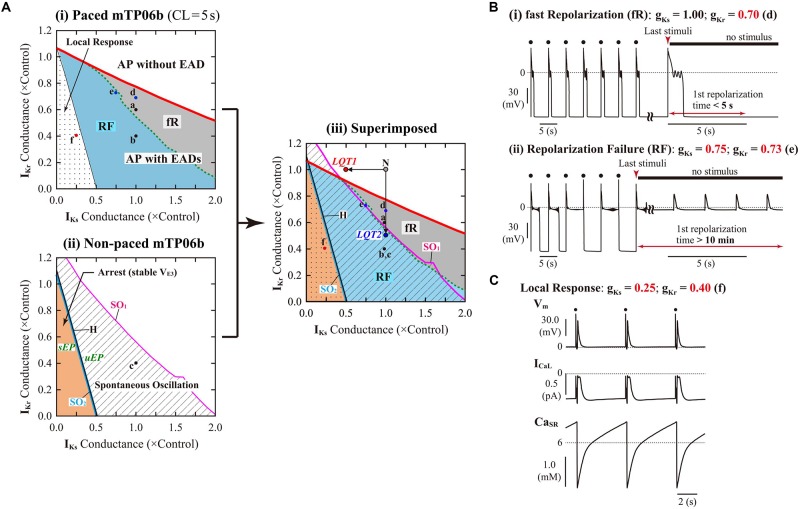
FIGURE 3.
IKr/IKs-dependent EAD formation, dynamics and bifurcations of the mTP06b model. (A) A phase diagram indicating the region of EAD formation (and local responses) in the paced model cell (i) and two-parameter bifurcation diagrams for the non-paced model cell (ii) on the gKs–gKr parameter plane. In the diagram for the paced model cell (i), the thick red solid, black dashed and thin black solid lines, respectively, indicate parameter sets of critical points at which short-term EADs (APD90 < 5 s, as in Figure 2A-a and [B-(i)], long-term or sustained EADs (APD90 > 5 s, as in Figure 2A-b and [B-(ii)], and a local response (C) emerged; parameter regions in which short-term EADs, long-term or sustained EADs, and local responses occur are shown as the light-gray region labeled as “fR” (fast repolarization), blue region labeled as “RF” (repolarization failure), and dotted region, respectively. In the two-parameter bifurcation diagram for the non-paced model cell (ii), H, SO1, and SO2 indicate parameter sets of HB points, critical points at which SOs emerged, and critical points at which SOs switched into quiescence, respectively. The parameter regions in which SOs and convergence to the steady state (VE3), i.e., arrest, can be observed are indicated as the shaded and orange regions, respectively. The labels “sEP” and “uEP” indicate the areas of stable and unstable EPs, respectively, divided by the HB curve. The panel (iii) is the diagram for which the phase diagram (i) is superimposed upon the two-parameter bifurcation diagram (ii). The points labeled as “N”, “LQT1” and “LQT2” denote the normal, LQT1, and LQT2 conditions, respectively. The points “a”–“f” indicate parameter sets for which AP behaviors are shown in Figures 2A-a–c, and [B (d,e)] [C (f)]. (B) Representative behaviors of APs with EADs during 0.2-Hz pacing at the points labeled as “d” and “e” in (A), which are classified into the fast repolarization type (d) and repolarization failure type (e) behaviors, respectively. (C) An example of the local response during 0.2-Hz pacing at the point “f” in (A).