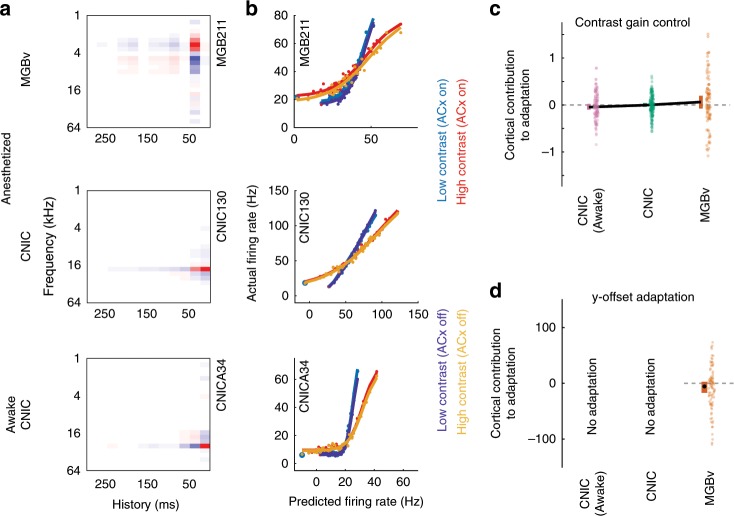
Fig. 5. Contrast adaptation in the CNIC and MGBv is unaffected by silencing of auditory cortex.
a Examples of spectro-temporal receptive fields of units recorded in MGBv and CNIC of anesthetized mice and in CNIC of awake mice (red: positive, white: 0, blue: negative). b The output nonlinearities of the same units during high- and low-contrast stimulation, with or without silencing of cortex. c Summary of effects of cortical silencing on contrast gain control in units recorded in MGBv and CNIC of anesthetized mice and CNIC of awake mice; this was quantified as the % gain change with cortex silenced minus the % gain change with cortex intact. d Summary of effects of cortical silencing on contrast-dependent y-offset adaptation in the MGBv; this was quantified as % adaptation with cortex silenced minus % adaptation with cortex intact. No contrast-dependent y-offset changes were observed in the CNIC, so the effects of cortical silencing are not shown. c, d Colored error bars, 95% bootstrapped non-parametric confidence intervals around the medians (individual data points (excluding outliers) are displayed next to the corresponding error bars). Source data for c, d are provided as a Source Data file.