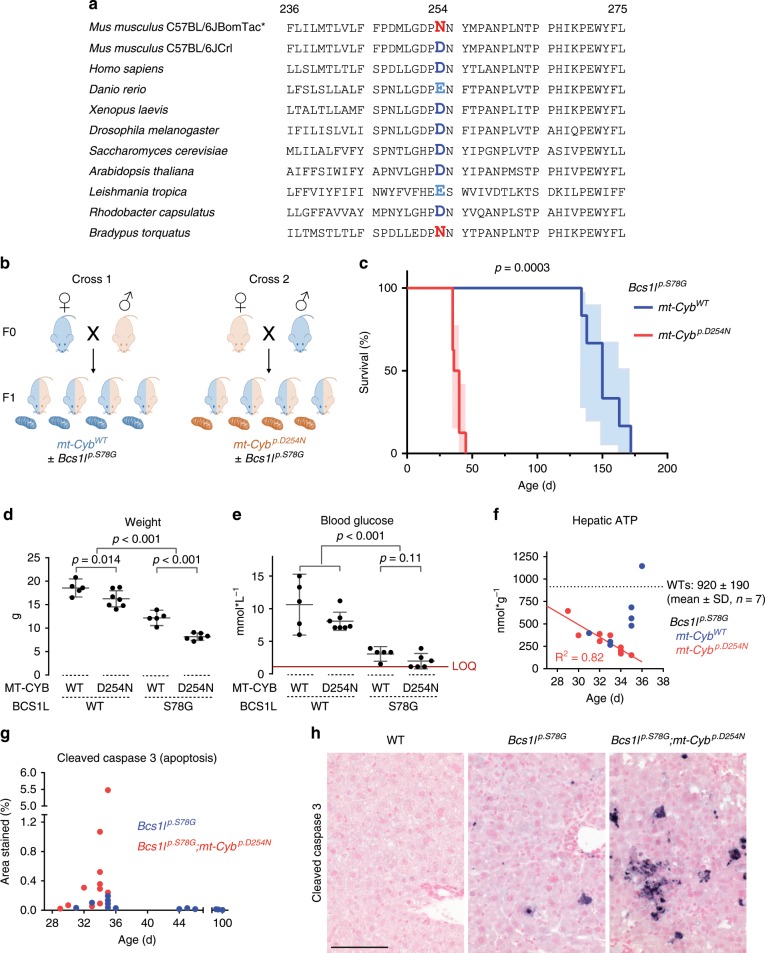
Fig. 1. Identification of a spontaneous mtDNA variant as a modifier of Bcs1l mutant phenotype.
a Alignment of amino acids 236–275 (numbering for Mus musculus sequence) of MT-CYB protein of various organisms. Asterisk (*), Lund in-house C57BL/6JBomTac-derived mouse colony. b Cartoon of the crosses to assess the effect of the maternally inherited mtDNA on the survival of Bcs1lp.S78G mice. c Survival analysis of Bcs1lp.S78G mice with either the C57BL/6JBomTac* (n = 8) or C57BL/6JCrl (Helsinki colony) maternal parent (n = 6). Light blue- and red-shaded areas illustrate 95% CI. d Weight and e blood glucose of juvenile F1 males. Three mt-Cybp.D254N-carrying Bcs1lp.S78G mice had blood glucose below the limit of quantification (LOQ, 1 mmol/l) of the glucose meter. f Hepatic ATP concentration of Bcs1l mutant mice with and without the mt-Cytbp.D254N variant plotted against mouse age. g The degree of hepatic apoptosis, cleaved caspase-3-positive cross-sectional area, plotted against age. h Representative micrographs of immunostained liver sections for cleaved caspase 3 from 34- to 35-day-old mice. Scale bar represents 100 µm. Statistics: c log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test, d one-way ANOVA followed by planned comparisons, e Kruskal–Wallis followed by Mann–Whitney U tests. Error bars represent 95% CI of the mean in all figures.