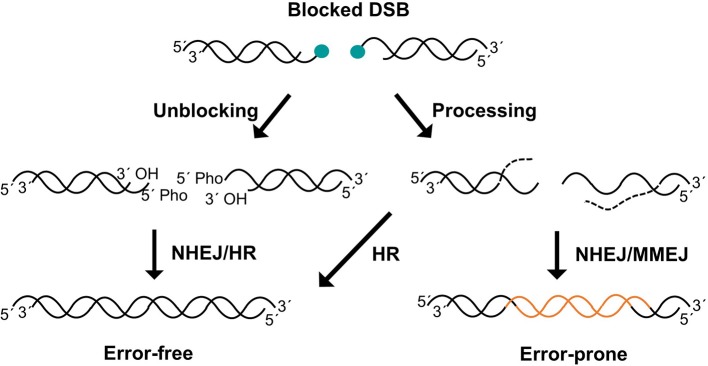
Figure 1.
Unblocking and processing of DSBs. Unblocking pathways directly convert ends into 5′-phospahte and 3′-hydroxyl but the nucleotide sequence remains intact, promoting error-free repair (left). Processing can also facilitate blocked DSBs repair removing aberrant structures from DNA ends by nucleotide trimming (right). This pathway can lead to error-prone repair when non-templated repair pathways such as NHEJ or MMEJ are used. 5′ blocks are depicted but similar situations could be generated on 3′ ends.