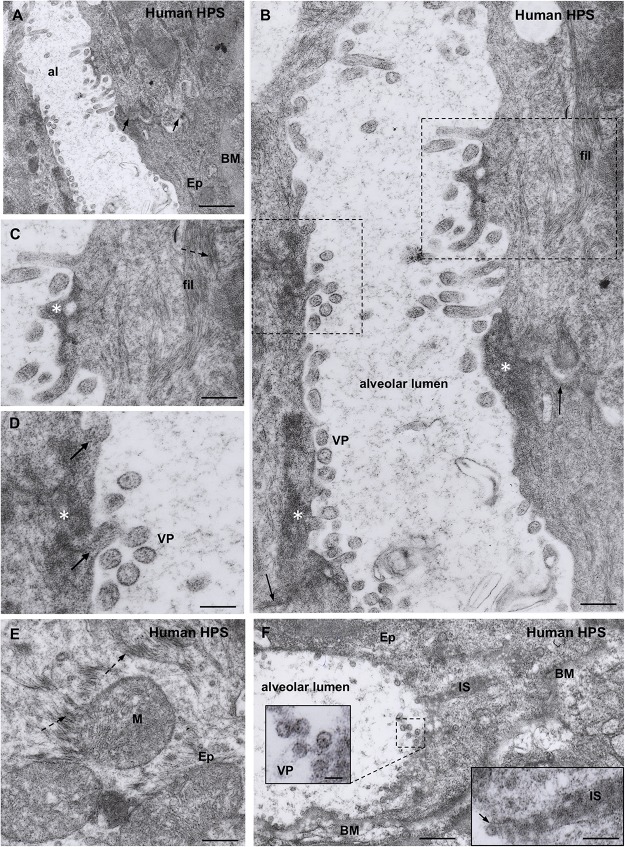
FIGURE 4.
Transmission electron microscopy of human lung from a lethal HPS case. (A) Low magnification view of the walls of an alveolum (al). The arrows point to the plasma membrane of neighbor epithelial cells (Ep). BM, basement membrane. Areas of this field are shown at higher magnification in the following figures. (B) Alveolar walls of the alveolum shown in (A). The cytoplasm of epithelial cells contains filamentous (fil) and granular (asterisks) inclusions. Virus-like particles (VP) and tubular structures appear lined along the apical domain of the plasma membrane. The arrows point to the plasma membrane of neighbor epithelial cells. (C) Detailed magnification of area framed by rectangle in B showing filamentous (fil, arrow) and granular (asterisk) inclusions. (D) Detailed magnification of area framed by square in B showing virus-like particles (VP) and granular inclusions (asterisk) that are in continuity with the content of tubular formations projecting to alveolar lumen (arrows). (E) Paranuclear region of an epithelial cell (Ep) showing the fine structure of the filamentous inclusions (broken arrows). (F) Alveolar epithelial cells (Ep) with isolated or clustered virus-like particles associated to the luminal cell surface. BM, basement membrane; IS, intercellular space filled with densely packed granulo-filamentous material. Left inset. Detailed view of virus-like particles (VP). Right inset. High magnification of electron dense material occupying a dilated intercellular space (IS) with a virus-like particle located at the luminal end (arrow). Scale bars. (A) 460 nm; (B) 175 nm; (C) 140 nm; (D) 105 nm; (E) 200 nm; (F) 370 nm, left inset 75 nm, right inset 180 nm.