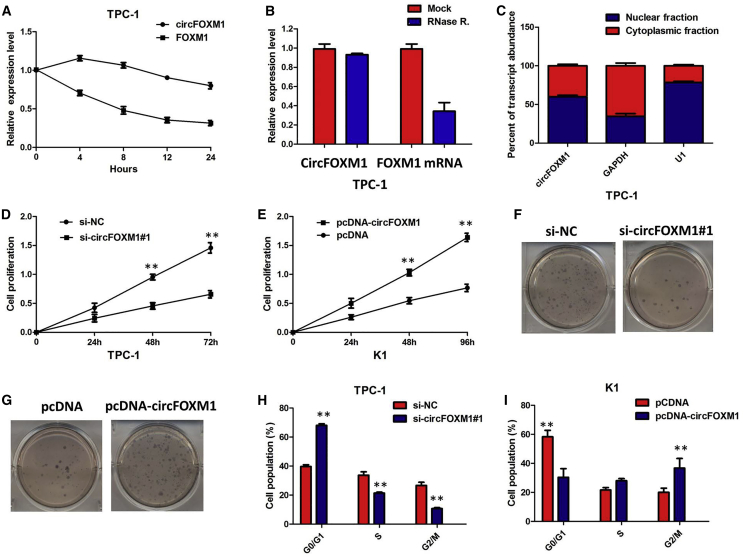
Figure 3.
circFOXM1 Promotes Cell Proliferation of PTC In Vitro
(A) qRT-PCR for the abundance of circFOXM1 and FOXM1 in TPC-1 cells treated with actinomycin D at the indicated time point. The error bars represent SD (n = 3). (B) qRT-PCR for the expression of circFOXM1 and FOXM1 mRNA in TPC-1 cells treated with or without RNase R. The results indicated that circFOXM1 was resistant to RNase R digestion. (C) Levels of circFOXM1 in the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of TPC-1 cells. The results showed that circFOXM1 was predominantly localized in the cytoplasm. Data are listed as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. **p < 0.01. (D) CCK8 assay showed that circFOXM1 knockdown significantly repressed cell proliferation of TPC-1 cells; **p < 0.01. (E) CCK8 assay showing that overexpression of circFOXM1 promoted the proliferation of K1 cells. (F) Colony-formation assay showed that the knockdown of circFOXM1 significantly restrained the proliferation of TPC-1 cells. (G) Colony-formation assay showed that the ectopic expression of circFOXM1 significantly promoted the proliferation of K1 cells. (H) The flow cytometry analysis showed that circFOXM1 knockdown led to an arrest in the G1 phase of TPC-1 cells; **p < 0.01. (I) The flow cytometry analysis showed that overexpression of circFOXM1 decreased the G0/G1-phase percentage of K1 cells; **p < 0.01.