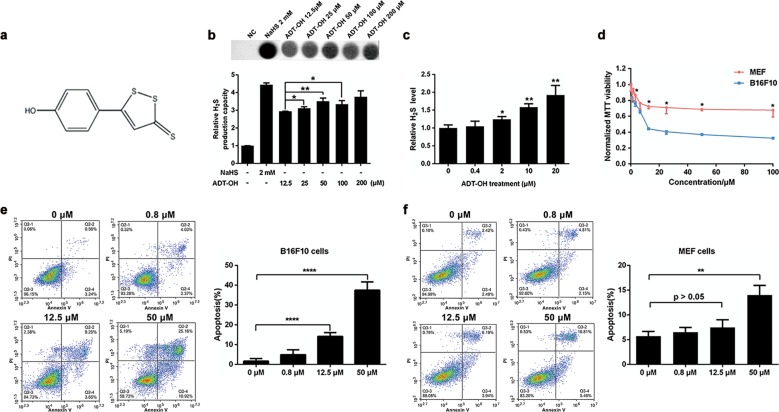
Fig. 1. ADT-OH inhibits melanoma cell proliferation and induces apoptosis.
a The chemical structure of ADT-OH. b H2S production capacity of ADT-OH acting on MEF cells via the lead sulfide method. c H2S measurement released by B16F10 melanoma cells after ADT-OH treatment in different concentration. d MEF and B16F10 melanoma cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of ADT-OH for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by CCK-8 assay. e B16F10 melanoma cells were treated with ADT-OH at different concentration (0.8–50 μM) and apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry analysis. And quantitative analysis of apoptosis at various concentrations of exposure to ADT-OH. Experiments (n = 3) were performed in triplicate. f Representative FACS analysis and quantitative analysis of Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) staining after ADT-OH treated at different concentration (0.8–50 μM) in MEF cells. Data are represented as mean ± SD for different experiments performed in duplicate. In b, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with ADT-OH 0.5 μM group; in c and d, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with vehicle group.