Figure 1.
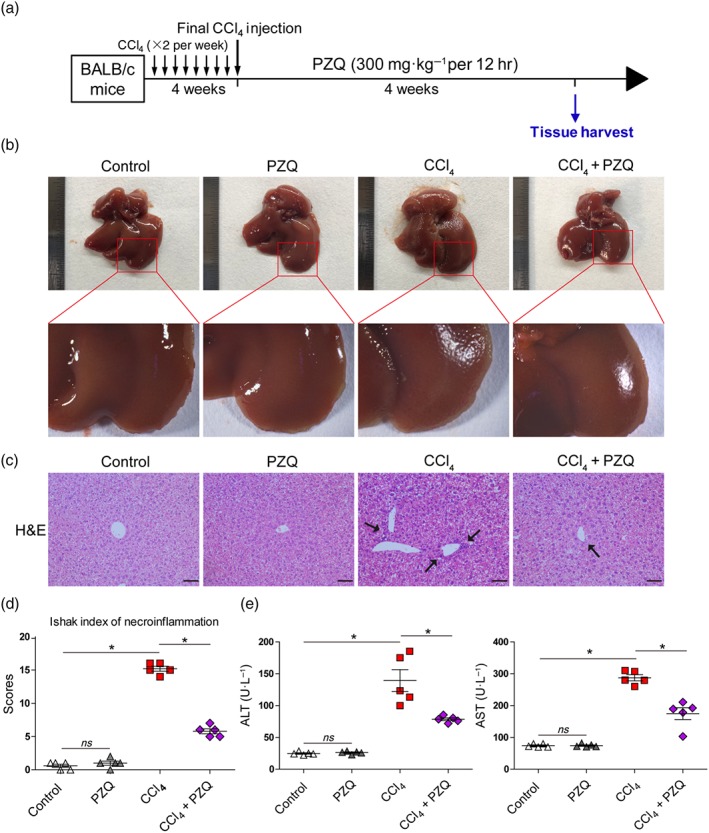
Praziquantel (PZQ) ameliorates functional and histological damage in CCl4‐induced liver injury. (a) Schematic representation of the liver fibrosis model in BALB/c mice induced by intraperitoneal CCl4 (1 ml·kg−1, diluted to 25% with olive oil) that was administered twice a week for 4 weeks, which was followed by intragastric administration of praziquantel (300 mg·kg−1 per 12 hr) for 4 weeks. The livers were harvested after the final administration. (b) Gross examination of the liver in mice with liver fibrosis that did or did not receive praziquantel. The ruler is on the left side of the diagram (n = 5). (c) Representative images of the liver sections stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E; arrows show examples of lobular inflammation). Scale bar, 100 μm. (d) Quantification of inflammatory changes according to the Ishak index scoring (n = 5). (e) Serum alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels after the final praziquantel administration (n = 5). All data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < .05, significantly different as indicated; ns, non‐significant
