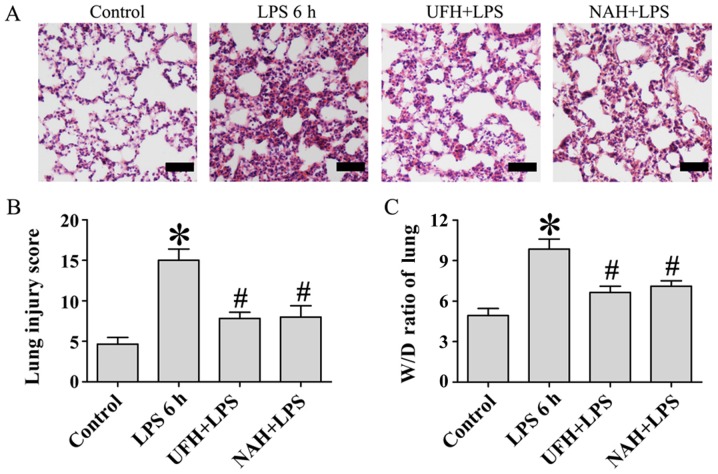
Figure 1.
Effect of heparin on histopathologic changes and lung W/D ratio in LPS-induced lung injury. Sprague-Dawley male rats were injected i.v. with UFH (100 U/kg) or NAH (1 mg/kg) and subsequently treated with LPS (10 mg/kg; 1 ml/kg of body weight; i.v.). Rats in the control group were injected i.v. with an equal volume of NS. A total of 6 h following LPS injection, the lung histopathologic changes were observed using (A) hematoxylin and eosin staining (n=6 rats/group; magnification, ×200; scale bar, 50 µm). (B) Lung tissues from each experimental group were processed and the lung injury score was used for histological evaluation. (C) The lung W/D ratios in each treatment group were quantified. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05 vs. the control group; #P<0.05 vs. the LPS 6 h group. Statistical comparisons were determined using a one-way analysis of variance followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test for multiple group comparisons. W/D, wet/dry; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; UFH, unfractionated heparin; NAH, N-acetylheparin; NS, normal saline; i.v., intravenous.