Figure 2.
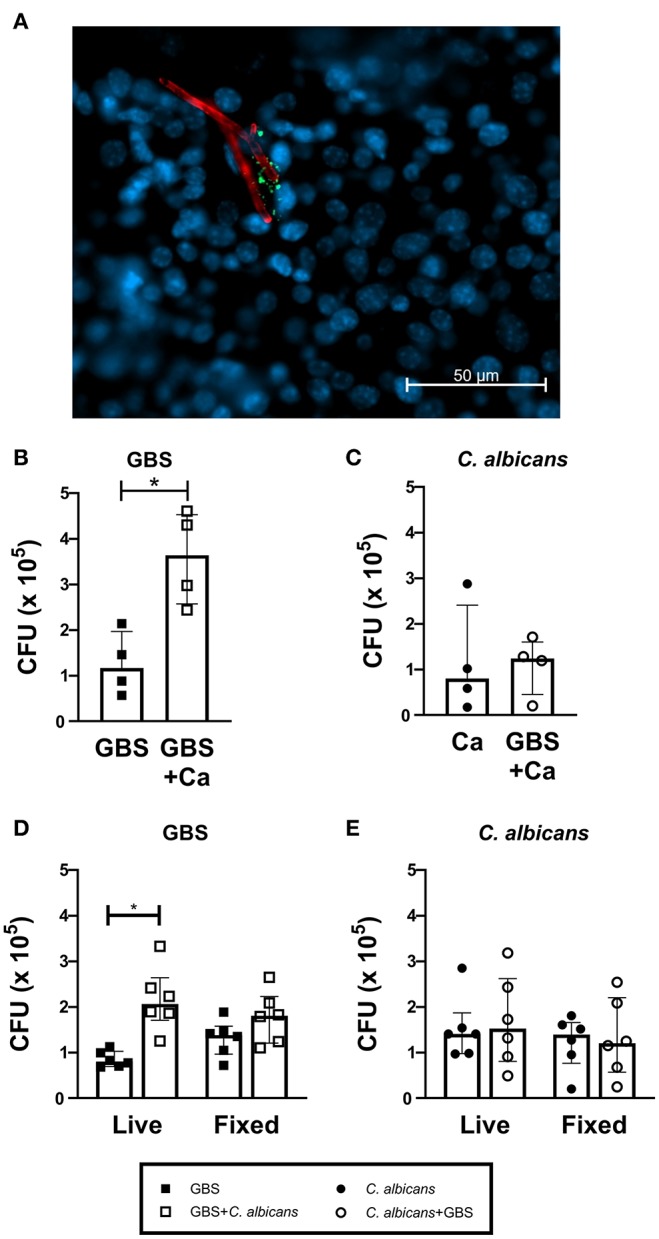
C. albicans and GBS coinfection increases bacterial adherence to bladder cells. (A) WT C. albicans SC5314 and GBS associate in vivo. C57Bl6/J female mice were infected with C. albicans and GFP-expressing GBS. Two hours later, bladders were harvested, fixed and stained for visualization via fluorescent microscopy. GFP-expressing GBS (green), AF594-anti-Ca antibody (red), and Hoechst dye (blue). Adherence of WT C. albicans SC5314 (B) and GBS (C) to human bladder epithelial cell line HTB-9 with single organism or mixed (GBS + C. albicans) inoculum. (D) GBS and (E) WT C. albicans SC5314 adherence of to live or fixed HTB-9 cells with single organism or mixed (GBS + C. albicans) inoculum. Data represent the means from four to five independent experiments performed in technical duplicate and are expressed as medians with interquartile ranges. Statistical analysis between experiments was performed using the Mann-Whitney test *P < 0.05.
