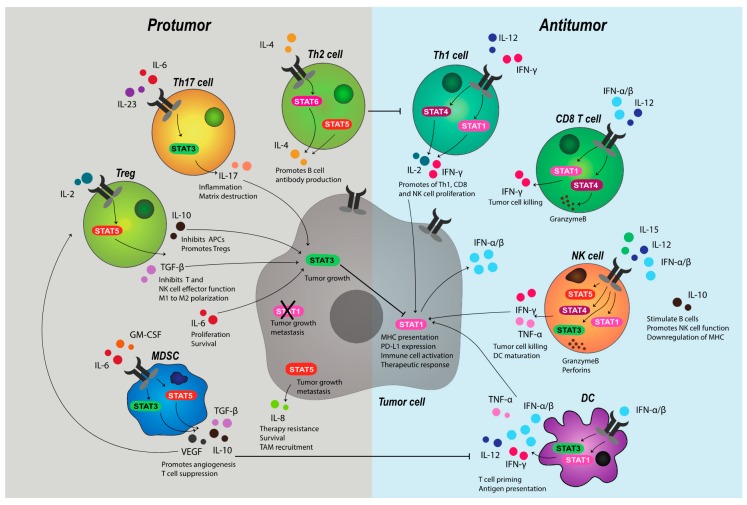
Figure 2.
STAT signaling in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Tumor cell fate is governed by tumor-inherent properties and the activity of surrounding immune cells, both of which are influenced by JAK-STAT signaling. A protumor immune microenvironment reflects a permissive niche and is comprised of populations including Th2 and Th17 cells, Tregs, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which signal mainly through STAT3 and STAT5 to produce inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-17, IL-10, TGF-β, or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). These cytokines can inhibit antitumor immune responses, promote TME suppression and act directly on tumor cells. High tumor cell STAT3 promotes tumor growth and metastasis, inhibits STAT1 signal transduction and leads to the production of protumor chemokines, cytokines and growth factors. Antitumor immune signaling is largely facilitated by cells involved in antigen recognition and directed cancer cell killing. Th1 cells, CD8 T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells (DCs) are all involved in antitumor immune responses through the secretion of cytokines, such as IFN-α/β, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2, along with perforins and granzymes, that induce tumor cell apoptosis, necrosis, T cell priming and antigen presentation. Cell-specific function and selective cytokine production is mainly regulated through STAT1 and STAT4. Acting on the tumor cell, these cytokines can signal through STAT1 to promote tumor immunogenicity via the upregulation of MHC and checkpoint proteins. Tumor cells themselves can also produce immune-stimulating cytokines, such as type I IFNs, to further promote immune infiltration and tumor visibility. Abbreviations: JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; Th, T-helper; Treg, regulatory T cell; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; IL, interleukin; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; TME, tumor microenvironment; NK, natural killer; DC, dendritic cell; IFN, interferon; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor-alpha; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1.