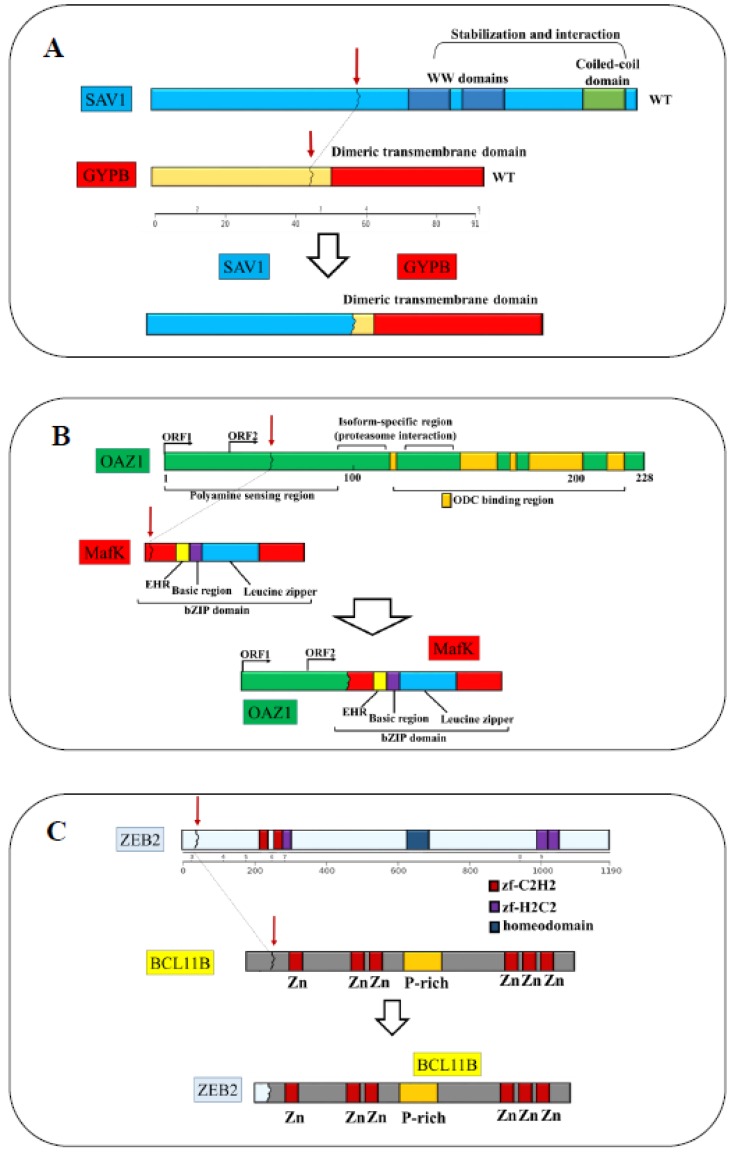
Figure 2.
Representation of the domains of the in-frame fusion genes. (A) The breakpoint of SAV1-GYPB mapped on chromosome 14p22, exon 2 of SAV1 (NM_021818) and chromosome 4q31, exon 2 of GYPB (NM_002100, Figure S1B). In the putative fusion protein, SAV1 lost the stabilization and interaction domains including the WW domain and the coiled-coil domain, while GYBP lost the N-terminal domains and retained the dimeric transmembrane domain. (B) The breakpoint of OAZ1-MAFK mapped in exon 1 of OAZ1 (NM_004152), which encodes for a polyamine sensing region and a proteasome interaction domain. The breakpoint at 3’ mapped in exon 2 of MAFK (NM_002360), which, together with exon 3, encodes for the bZIP domain. The putative chimeric protein was formed by the sensing regions of polyamine that normally controls the transcription of OAZ1, and the bZIP domain of MAFK. (C) The breakpoint of the fusion ZEB2-BCL11B mapped in exon 2 of ZEB2 (NM_014795) and exon 2 of BCL11B (NM_00128223). Twenty-four residues of ZEB2 and 803 out of 823 residues of BCL11B formed the fusion protein. The codon 20 of BCL11B was the first involved in the fusion and it encoded for an alanine instead of a proline, due to a single nucleotide substitution at the breakpoints junctions (yellow dot).