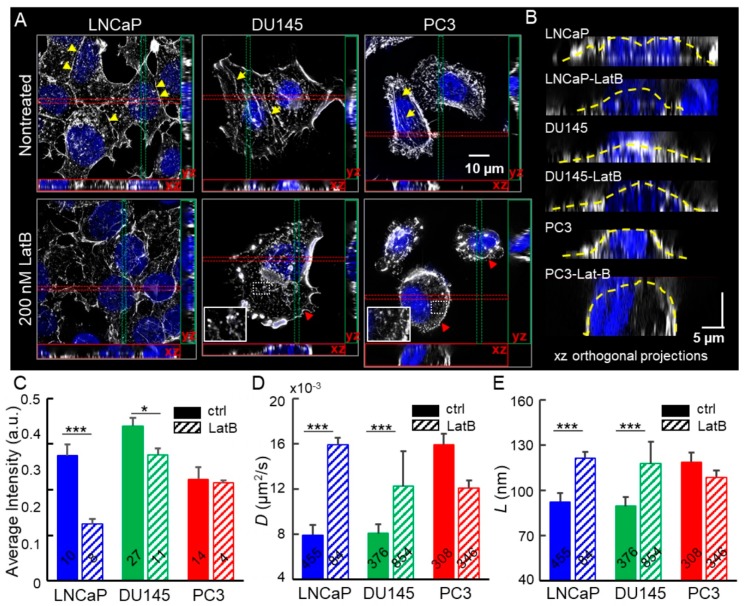
Figure 2.
Depolymerization of F-actin induces increased EGFR diffusivity and compartment size. (A) Maximum intensity projection on the xy plane, and orthogonal cross-sections (xz and yz) of LNCaP, DU145, and PC3 cells before and after Latrunculin B (LatB) treatment. LatB inhibits the polymerization of F-actin. The yellow arrowheads, yellow arrows, and red arrows pinpoint the peri-junctional actin bands, the stress fibers on the basal side of cells, and the filopodia, respectively. (B) The xz projections clearly show the dissociation of cortical actin from the apical surface of the plasma membrane after LatB treatment. (C) Quantification of cortical actin based on fluorescence intensities of xz and yz orthogonal projections along the apical plasma membrane (shown as the yellow dashed line in (B)). The fluorescence intensities are normalized and presented as an arbitrary unit (a.u.). The number of projections analyzed is labeled on each bar. (D) Diffusion coefficients of EGFRs extracted from trajectories. The number of trajectories analyzed is labeled on each bar. (E) The linear dimension of confinement extracted from EGFR trajectories. All statistical analyses were performed using the unpaired t-test. The asterisk represents the level of statistical significance for t-test: * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001. The error bar represents the standard error of the mean.