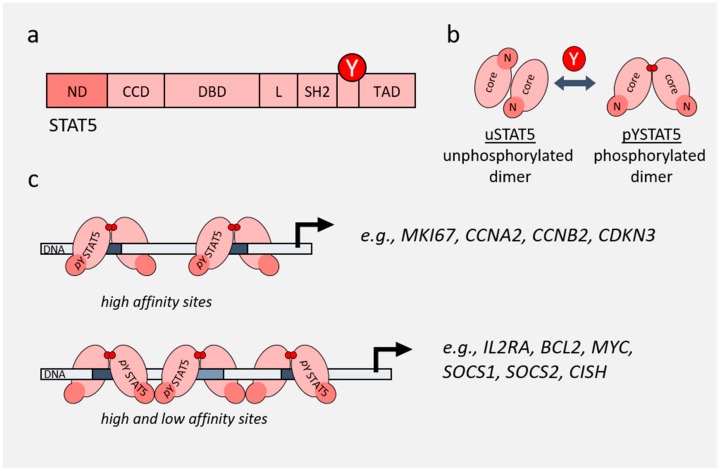
Figure 1.
Functions of STAT5. (a) Domain structure of STAT5. Position of the critical activating tyrosine phosphorylation site is depicted with Y. ND—N-domain; CCD—coiled-coil domain; DBD—DNA-binding domain; L—linker; SH2—SH2 domain; TAD—transactivation domain. (b) Conformational changes of STAT5 from an unphosphorylated antiparallel dimer (uSTAT5) to a phosphorylated parallel dimer (pYSTAT5). (c) Dimer and oligomer conformations of STAT5 result in binding to GAS sites on DNA with different affinities, resulting in expression of different genes. Examples of dimer versus tetramer target genes are incorporated from [32,33].