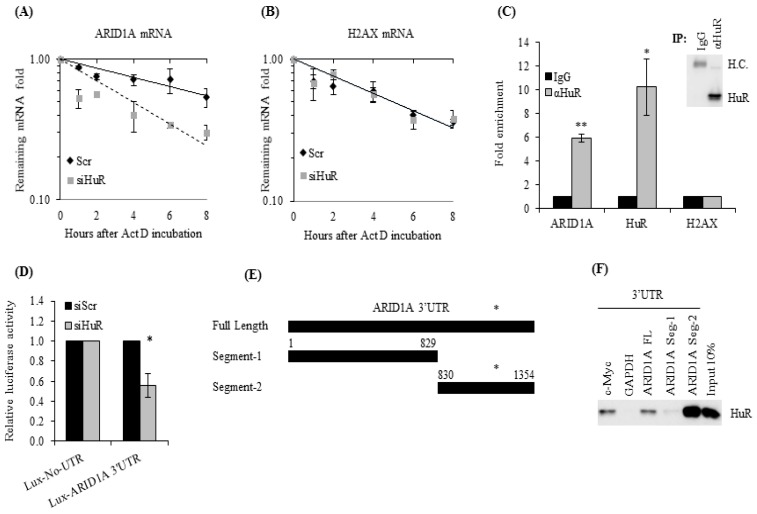
Figure 1.
ARID1A is a bona fide human antigen R (HuR) target. (A) Twenty-four hours after transfection with siHuR, MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with Actinomycin D and collected at the indicated time points to evaluate their ARID1A mRNA levels by RT-qPCR. (B) H2AX mRNA levels were also evaluated as a negative control. (C) MDA-MB-231 cell lysates were used to immunoprecipitate HuR using an antibody against HuR or IgG. HuR immunocomplexes were subjected to RNA extraction, and the levels of ARID1A mRNA were measured by qRT-PCR. The levels of HuR and H2AX mRNAs were also measured as positive and negative controls, respectively. Inset shows HuR immunoprecipitation by HuR antibody, but not by IgG control. (D) Eight hours after transfection with HuR siRNA, MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with a vector encoding either luciferase alone (Lux-No-UTR) or luciferase fused to the 3′UTR of ARID1A (Lux-ARID1A 3′UTR); 16 h later, luciferase activity was evaluated. (E) Three segments of ARID1A 3′UTR were cloned into a T7 containing vector to generate biotinylated RNA probes. Asterisk indicates regions of high probability for HuR binding. (F) These probes were incubated with MDA-MB-231 lysates, recovered with neutravidin-coated beads, and subjected to immunoblot analysis to evaluate the levels of HuR bound to the probes. Data represent the average of three independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM (standard error of the mean), * p ≤ 0.01 and ** p ≤ 0.001.