Figure 2.
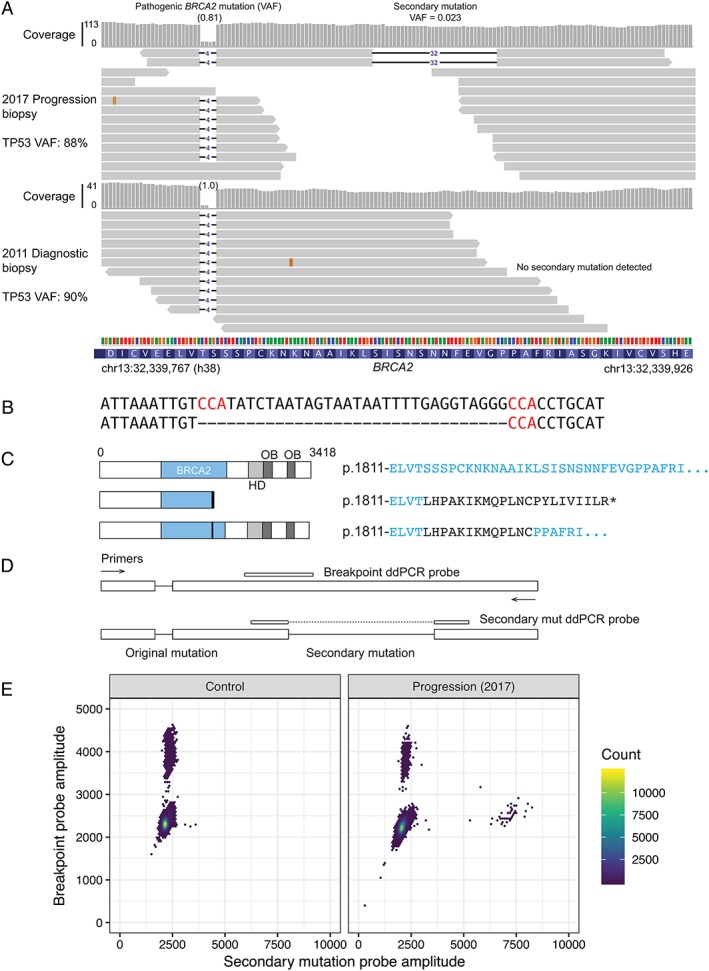
Secondary mutation restoring the BRCA2 reading frame in a peritoneal biopsy at progression. (A) Alignments of exome sequencing read to the region around the original somatic BRCA2 mutation. Top, progression biopsy (2017, fresh frozen); bottom, diagnostic biopsy (2011, FFPE, micro‐dissected). The two reads with an additional 32 bp deletion observed in the recurrence sample are shown along with a sample of other reads. (B) DNA sequence of reference (top) and secondary mutant (bottom) at site of deletion. Flanking microhomology is highlighted in red. (C) Predicted effect of original and secondary mutations on the BRCA2 protein. HD, BRCA2 helical domain; OB, OB fold DNA binding domain. Amino acids unique to the mutant proteins are shown in black. (D) ddPCR assay design for detection of the candidate secondary mutation. (E) Scatter plots for ddPCR assay in (D). Left panel shows the CAL51 cell line as a control. Right panel shows peritoneal biopsy at progression (as in A).
