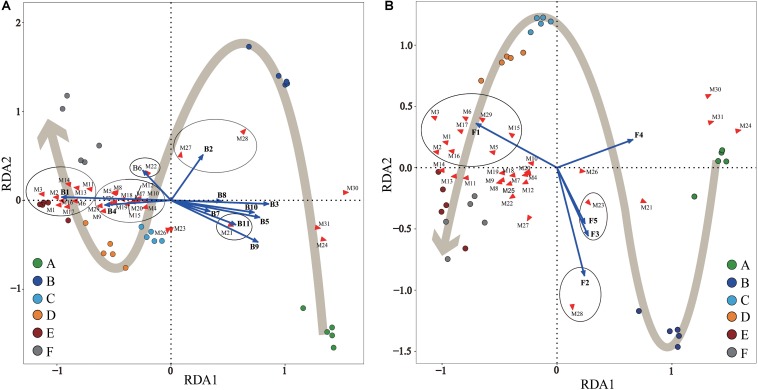
FIGURE 5.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of Panxian ham samples, core microbial genera, and significantly different metabolites (SDMs) during Panxian ham processing. (A) Correlation between samples, core bacteria genera, and SDMs. (B) Correlation between samples, core fungi genera, and SDMs. A–F indicate the traditional spontaneous fermentation process stage of Panxian ham: (A) raw ham; (B) post-salting; (C) post-resting; (D) initial stage of ripening; (E) middle stage of ripening; (F) final stage of ripening. The core bacterial and fungal genera were consistent with Figures 4C,D; while SDMs are represented by M1–M31. M1, valine; M2, Isoleucine; M3, proline; M4, glycine; M5, serine; M6, L-allothreonine; M7, aspartic acid; M8, methionine; M9, pyroglutamate; M10, glutamic acid; M11, phenylalanine; M12, ornithine; M13, lysine; M14, tyrosine; M15, alanine; M16, myristic acid; M17, palmitoleic acid; M18, heptadecanoic acid; M19, arachidonic acid; M20, arachidic acid; M21, stearic acid; M22, succinic acid; M23, malic acid; M24, creatine; M25, glycerol; M26, myo-inositol; M27, fructose; M28, glucose; M29, hypoxanthine; M30, inosine; M31, creatinine.