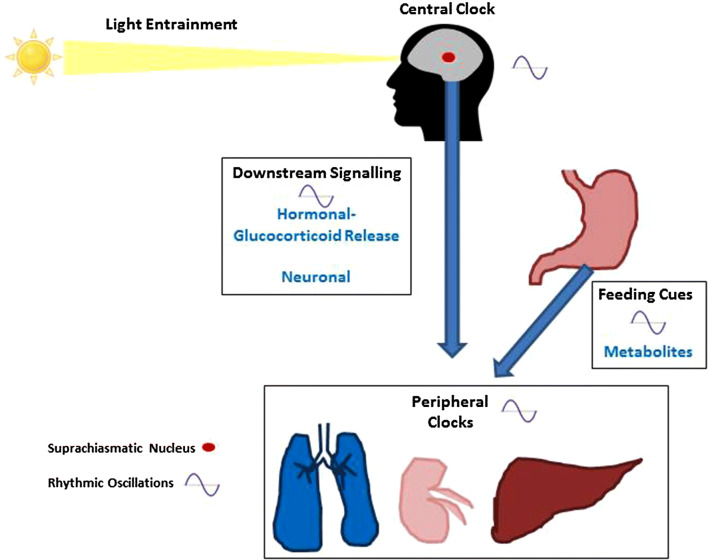
Fig. 1.
The central and peripheral clocks. The ‘central’ clock or pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain integrates light and dark information and relays the information downstream to ‘peripheral’ clocks found in virtually every cell in the body, by a network involving neural pathways, hormone release (glucocorticoids), and metabolic cues from rhythmic feeding behavior. Light is the key entrainment factor for the SCN and feeding-regulated metabolic cues are pivotal for the regulation of many peripheral clocks