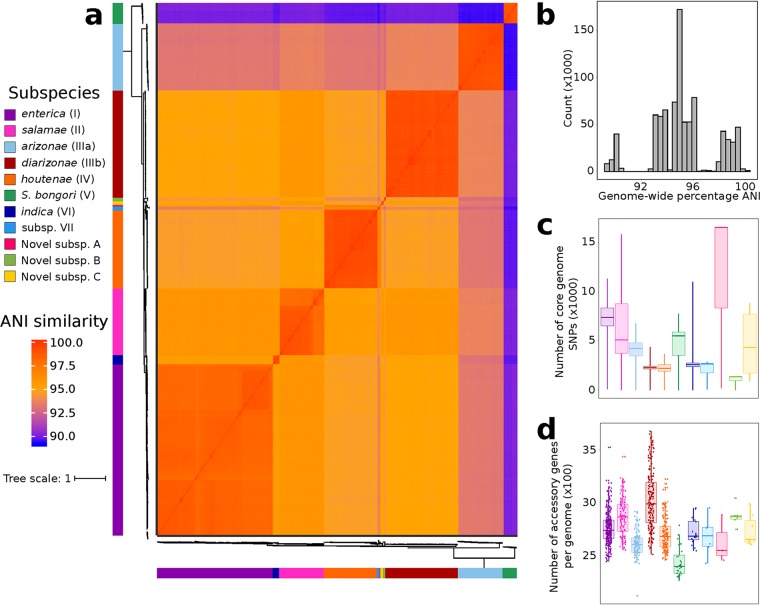
FIG 1.
Genomic differences among Salmonella enterica subspecies genomes. (a) Pairwise genome-wide ANI values. ANI calculates the average nucleotide identity of all orthologous genes shared between any two genomes. The phylogeny was reconstructed using the concatenated alignment of 1,596 genus-wide core genes. The scale bar represents nucleotide substitutions per site. (b) Frequency distribution of all pairwise ANI values. The 95% ANI cutoff is a frequently used standard for species demarcation. (c) Number of SNPs in the core genome alignment per subspecies. The box shows the median SNP count and the lower and upper quartiles. The whiskers represent the minimum and maximum SNP counts. (d) Number of accessory genes per genome for each subspecies. Subspecies classification is based on core genome variation calculated by Alikhan et al. (12).