Figure 1.
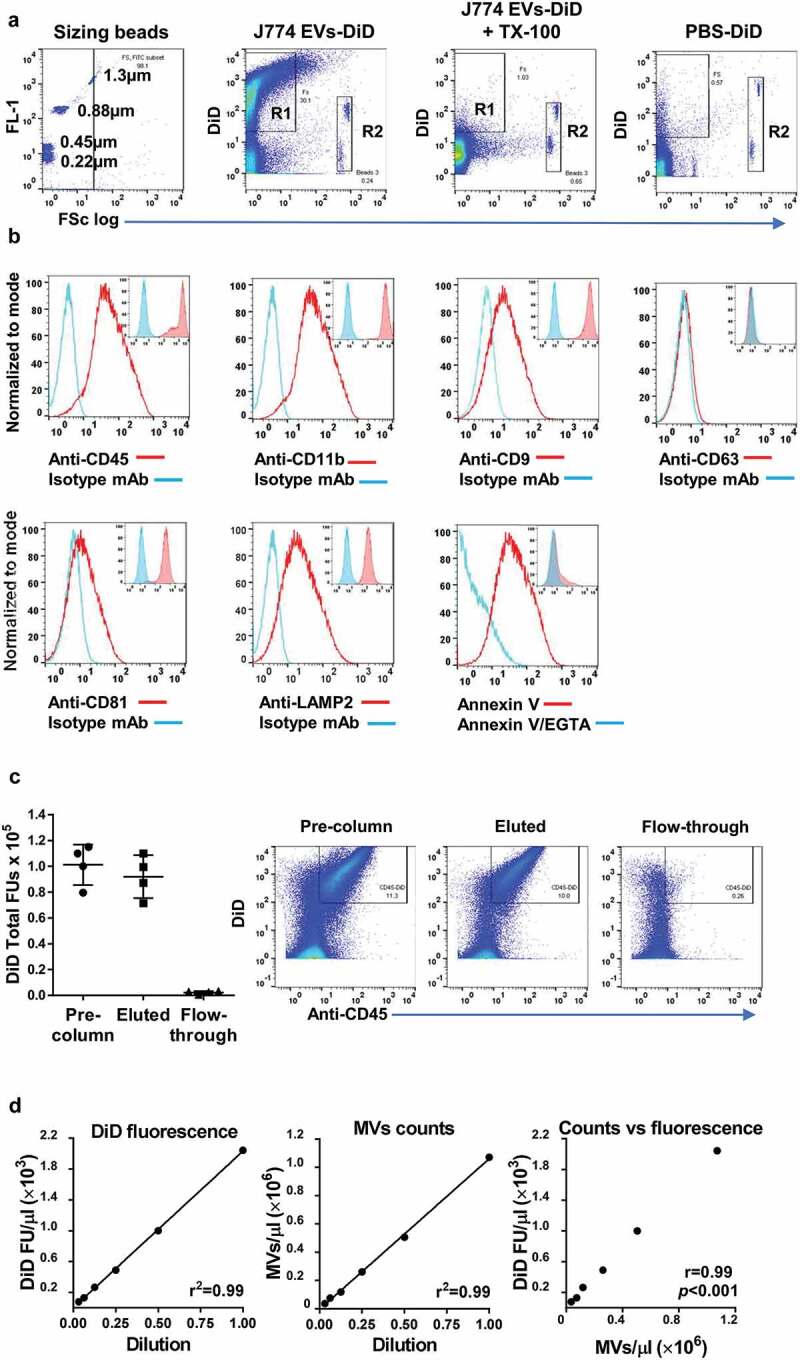
DiD-labelling and analysis of ATP-induced J774 EVs. J774 cells were stimulated with ATP (3 mM, 30 min), and the released EVs labelled with DiD and analysed by flow cytometry. (a): Comparison with fluorescent sizing calibration beads (Sperotech) indicated that the forward scatter (FSc) of most DiD-positive events (R1) was lower than that of the 1.3 µm beads and all lower than the ~6 µm diameter Accucheck counting beads (R2). Incubation of samples with non-ionic detergent (Triton X-100, 0.1%) resulted in the disappearance all DiD-positive events consistent with their vesicular nature [78], while incubation and centrifugation of DiD in buffer without EVs (PBS-DiD) produced relatively few fluorescence-positive events (b): The subcellular origin of DiD-positive J774 EVs was assessed by staining with phycoerythrin-conjugated monoclonal antibodies (mAb) against typical myeloid cell membrane (CD45, CD11b) and exosome (CD9, CD63, CD81, LAMP2) markers. Positive staining of EVs (main histogram overlays) corresponded well to the staining pattern of viable untreated J774s (inset histogram overlays), suggesting DiD-positive EVs were derived mainly from the plasma membrane. Note that J774 cells do express CD9, CD81 and LAMP2, but not CD63 on their surface. Surface exposure of phosphatidylserine (PS) on DiD-labelled EVs was evident from their staining with FITC-conjugated annexin V and its reversal by incubation with the calcium cation chelator EGTA (5 mM). (c): The majority of DiD fluorescence in labelled samples was present in CD45+ EVs bound to and eluted from anti-CD11b conjugated immunomagnetic microbeads, with very low levels of fluorescence in the unbound column flow-through. (d): Serial 2-fold dilutions of DID-labelled EV preparations indicated linearity and correlation (Pearson correlation coefficient) in the detectable range of DiD fluorescence units (FU) measurement and the flow cytometric MV counts (DiD/CD11b double-positive events).
