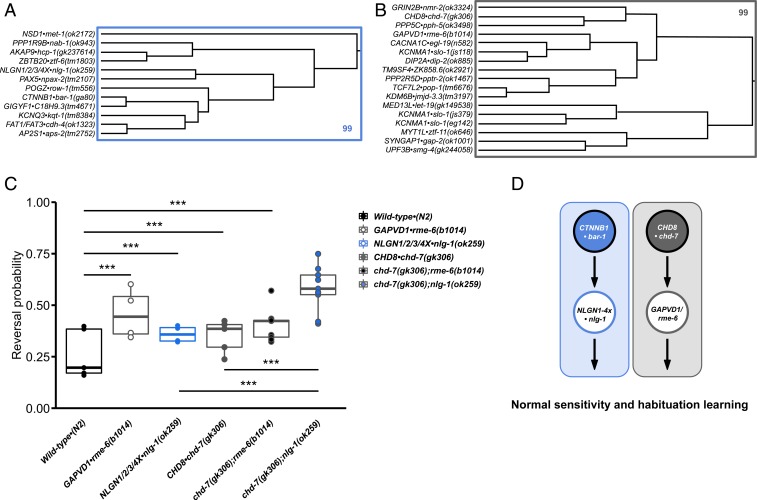
Fig. 4.
Combining phenotypic clustering and epistasis analysis to map parallel genetic networks underlying hyperresponsivity and impaired habituation. (A and B) Hierarchical clustering based on sensory and learning features identified 2 sets of genes with members that display impairments in habituation of response probability and hyperresponsivity to mechanosensory stimuli (increased initial reversal response duration). Rectangles outline the largest clusters with AU P values >95%. (C) Final reversal probability across genotypes (average of the 28th to 30th responses). Dots represent individual plate means, and horizontal lines represent median of plate replicates. Binomial logistic regression followed by Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) criterion was used to determine significance of the habituated level (proportion reversing at tap 30) for each pair of strains (***P < 0.001). (D) Parallel genetic pathways of ASD-associated genes underlie impaired habituation learning.