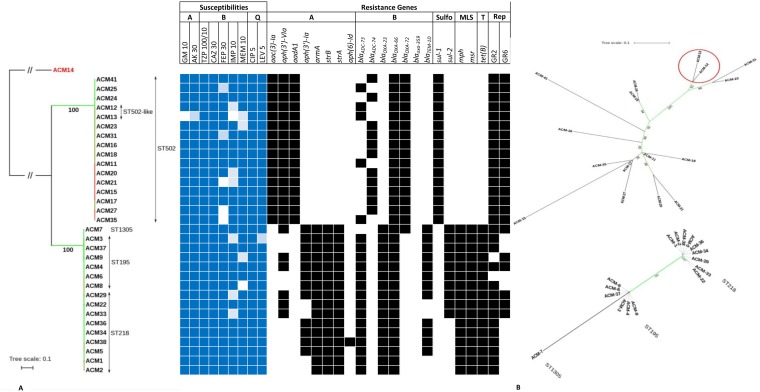
FIG 2.
Maximum-likelihood phylogeny based on SNPs across A. baumannii isolates. (A) Branch lengths are proportional to the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. Bootstrap values are indicated by numbers below branches as well as by branch coloring (green, high confidence levels; red, low confidence levels). Dashed lines connect labels with particular leaf nodes in order to avoid labels to overlap the branches. Classes of antibiotics are given the following markings: A, aminoglycosides; B, β-lactams; Q, quinolones; T, tetracyclines; GM, gentamicin; AK, amikacin; TZP, piperacillin-tazobactam; CAZ, ceftazidime; FEP, cefepime; IMP, imipenem; MEM, meropenem; CIP, ciprofloxacin; LEV, levofloxacin. Dark blue indicates resistant, light blue indicates intermediate susceptibility, and blank indicates sensitive. (B) Unrooted phylograms inferred from SNP data from core genomes of strains belonging to the Tn2006-mediated clone and cluster pMAL-1-mediated clone, respectively. Red circle in the pMAL-1-mediated clone highlights ST-2059 isolates. Bootstrap values are indicated by numbers below branches as well as by branch coloring (green, high confidence levels; red, low confidence levels). Dashed lines connect labels with particular leaf nodes in order to avoid labels to overlap the branches.