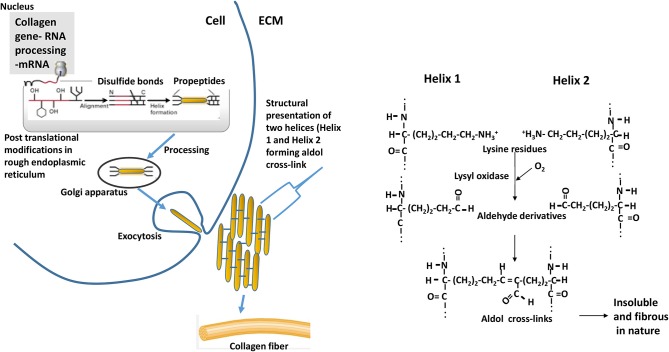
Figure 10.
Events depicting the biosynthesis of fibrous collagens. Pre-procollagen polypeptides (α-helical region colored red) synthesized in nucleus go through events of post-translational modifications (hydroxylation and glycosylation) of certain proline and lysine residues to 4-hydroxyproline, 3-hydroxyproline, hydroxylysine, galactosylhydroxylysine, and glucosylgalactosylhydroxylysine. Catalyzing enzymes responsible for hydroxylation are prolyl 4-hydroxylase, prolyl 3-hydroxylase, and lysyl hydroxylase; whereas galactosyl transferase and glucosyltransferase are involved in glycosylation. Disulfide bonds formation (at C-terminal) among three procollagen polypeptides results in initiation of triple helix structure. Further processing of helix occurs in golgi apparatus, and then processed helix is exocytosed to extracellular matrix (ECM). Helices align laterally (presented as Helix 1 and Helix 2 in the schematics) and interact forming aldol cross-links between two lysine (or hydroxlysine) residues to form collagen fibrils. ECM = extracellular matrix. The reaction is catalyzed by enzyme lysyl oxidase. Adapted with modifications from Lodish et al. (27).