Fig. 3. Effect of hydrophilic particle contamination having various particle sizes deposited from ethanol dispersion on nanoporous superhydrophobic surfaces.
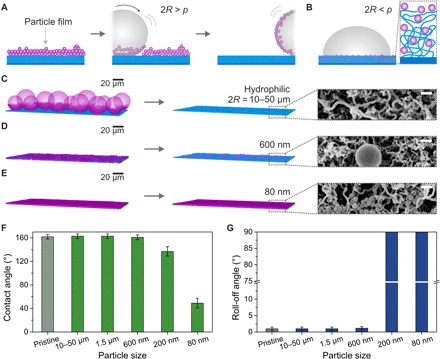
(A) Schematic illustration of the self-cleaning process of hydrophilic particles (purple; 2R > p) deposited from ethanol dispersion by a water drop (gray). (B) Particles of smaller diameter than the pore diameter (2R < p) can penetrate the coating (blue), affecting wetting properties. (C to E) LSCM images (left) after contamination of the superhydrophobic surfaces with hydrophilic particles with diameters of 10 to 50 μm, 600 nm, and 80 nm (see Materials and Methods and fig. S9 for details of image processing). LSCM (center) and SEM images (right) show the surfaces after rinsing. Scale bars, 200 nm (SEM). (F and G) Contact and roll-off angles using 6-μl water drops after self-cleaning of nanoporous surfaces contaminated with various hydrophilic particles (dried from ethanol dispersion).
