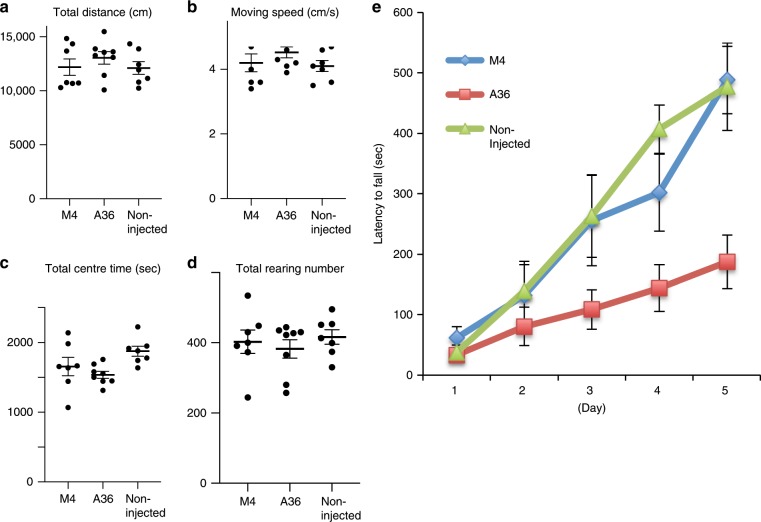
Fig. 8. STAND-A36 impairs motor-skill learning.
a–d Open-field test. Total distance travelled a, moving speed b, total time spent in the centre of the field c, and total number of rearings d are shown. e Rotarod test. Latency to fall is shown. Statistical analysis in a–d; two-tailed one-way ANOVA: Total distance, F (2, 19) = 0.6885, P = 0.51441; moving speed, F (2, 19) = 1.19321, P = 0.32476; total number of rearings, F (2, 19) = 0.40367, P = 0.67345; total centre time, F (2, 19) = 3.79839, P = 0.04095, Tukey’s multiple comparison test, A36 vs. non-injected, P = 0.033782; A36 vs. M4, P = 0.612174; M4 vs. non-injected, P = 0.223909. Statistical analysis in e; two-tailed two-way ANOVA: interaction, F (8, 76) = 2.890, P = 0.0072677; gene, F (2, 19) = 6.208, P = 0.00842; time, F (2.771, 52.66), P < 0.00001, Tukey’ multiple comparison test, Day 5, A36 vs. M4, P = 0.0053325; A36 vs. non-injected, P = 0.0247076; M4 vs. non-injected, P = 0.9933278, M4, Day 1 vs. Day 5, P = 0.002306; A36, Day 1 vs. Day 5, P = 0.0885538; non-injected, Day 1 vs. Day 5, P = 0.007349. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.