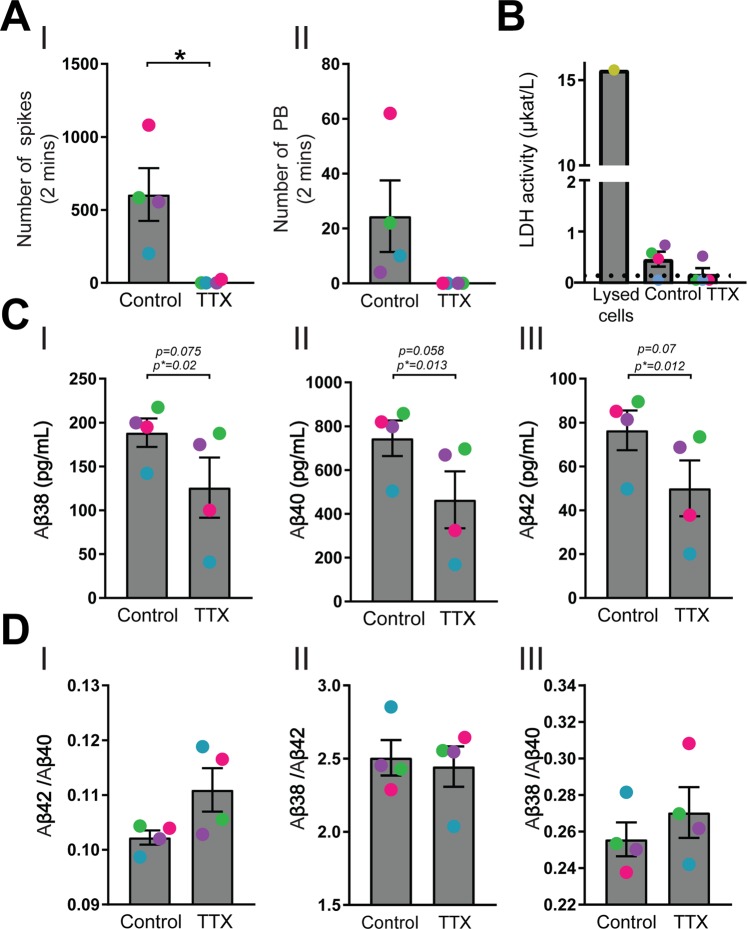
Figure 6.
Tetrodotoxin blocks synaptic activity and decreases Aβ secretion. Neurons cultured in BrainPhys for ten days were treated with 1 µM tetrodotoxin (TTX) for 24 hours and the effects of synaptic activity on secreted Aβ peptides analyzed. (A) The number of spikes (I) and population bursts (II) are still decreased after 24 hours of TTX treatment, showing a prolonged blockage of synaptic activity with TTX. (B) Released lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) into the cell-conditioned media, measured with LDH activity assay on the cell media to exclude TTX-induced cell death. No significant differences in LDH release are observed between control- and TTX-treated neurons. As a positive control, cells lysed in 1% (v/v) Triton-X100 to release all LDH is included. Samples under the limit of detection of 0,17 µkat/L (shown with black dotted line), are plotted as 0.085 (half of the value for the limit of detection). (C) The secretion of Aβ38 (I), Aβ40 (II) and Aβ42 (III) decreases in all experiments with TTX, as compared to vehicle control. “p” indicates un-normalized p values whereas “p*” indicates p-value for data normalized to the control. (Each experiment is marked with separate colours to show the individual effect). (D) The ratios of Aβ42/40 (I), Aβ38/42 (II) and Aβ38/40 (III) do not change significantly by TTX treatment. Mean values of four separate experiments on neurons from two different iPSC lines (ChiPSC22 marked with pink circles and WTSIi015-A marked with green, blue and purple circles) were analysed with Student’s t-test. Bars represent mean +/− SEM. *p ≤ 0.05.