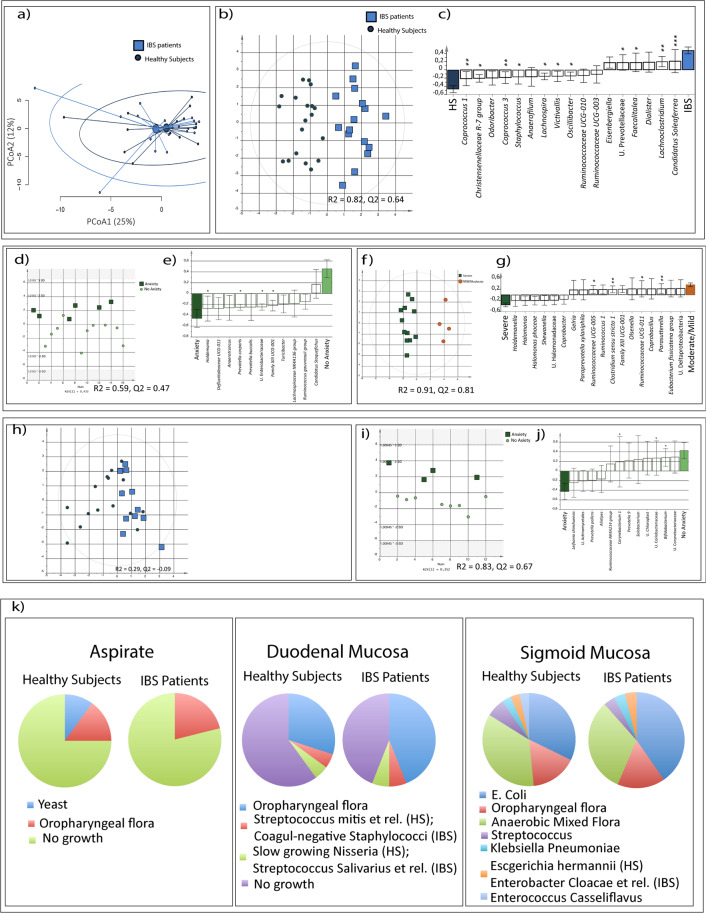
Figure 3.
Mucosa-associated bacterial profiles and SIBO evaluation of IBS patients and healthy subjects. (a) PCA of the mucosa-associated bacterial composition of the colon of IBS and healthy. (b) Score scatter plot from the Multivariate orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) showing the separation between IBS (n = 16, light blue squares) and healthy (n = 19, dark blue cicles), respectively, and the mucosa-associated bacterial composition in the colon. (c) OPLS-DA loading column plot of the mucosa-associated bacteria of the colon that contributed the most to the separation between IBS and healthy. (d) Score scatter plot from the OPLS-DA showing the separation between IBS patients with anxiety (n = 6; dark green squares), and without anxiety (n = 10, light green circles), respectively, and the mucosa-associated bacterial composition in the colon. (e) OPLS-DA loading scatter plot of the mucosa-associated bacteria of the colon that contributed the most to the separation between IBS patients with and without anxiety. (f) Score scatter plot from the OPLS-DA showing the separation between symptom severity (IBS-SSS) based IBS subsets, mild/moderate IBS (IBS-SSS < 300, n = 4; orange circles) and severe IBS (IBS-SSS > 300, n = 12, green squares) respectively, and the mucosa-associated bacterial composition of the colon. (g) OPLS-DA loading column plot of the mucosa-associated bacteria of the colon that contributed the most to the separation between IBS patients with severe symptoms compared to those with mild/moderate symptoms. (h) OPLS-DA score scatter plot of the mucosa-associated bacterial composition of the duodenum of IBS (n = 12, light blue squares) compared to healthy (n = 19, dark blue circles). (i) OPLS-DA score scatter plot depicting the association between IBS patients with anxiety (n = 4; dark green squares), and without anxiety (n = 8, light green circles), respectively, and the mucosa-associated bacterial composition in the duodenum. (j) OPLS-DA loading scatter plot of the mucosa-associated bacteria of the duodenum that contributed the most to the separation between IBS patients with and without anxiety. (k) Proportions of bacterial growth in aspirates, duodenal biopsies and colonic biopsies, respectively in IBS (n = 16) and healthy (n = 19). * = Significant difference between groups according to the Mann-Whitney test or the Kruskal-Wallis test. U. = Unclassified.