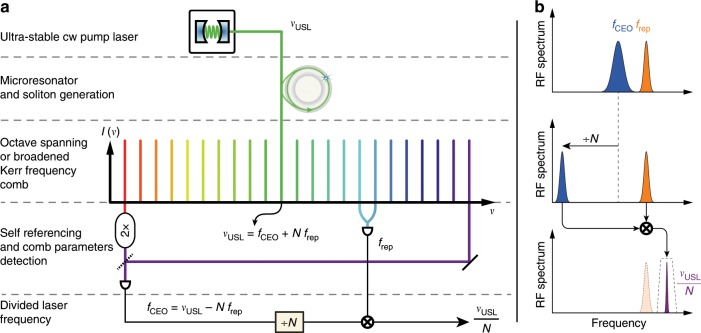
Fig. 1. Principle of operation of the Kerr comb-based transfer oscillator.
for optical-to-microwave frequency division. a Schematic illustration of the transfer oscillator applied to a Kerr comb (or electro-optic combs equivalently). b Schematic representation of the signal evolution along the electronic division chain leading to the low-noise output signal. The two comb parameters fCEO and frep are detected. Both parameters can be free-running and fluctuate. The carrier envelope offset (CEO) frequency is electronically divided by a large number N that corresponds to the tooth number of the ultra-stable pump νUSL. After this step, the frequency fluctuations of the divided CEO fCEO∕N = νUSL∕N − frep are dominated by the repetition rate fluctuations. These are removed by mixing fCEO∕N with frep to obtain the division result νUSL∕N. A narrow-band filtering is used to reject spurs.