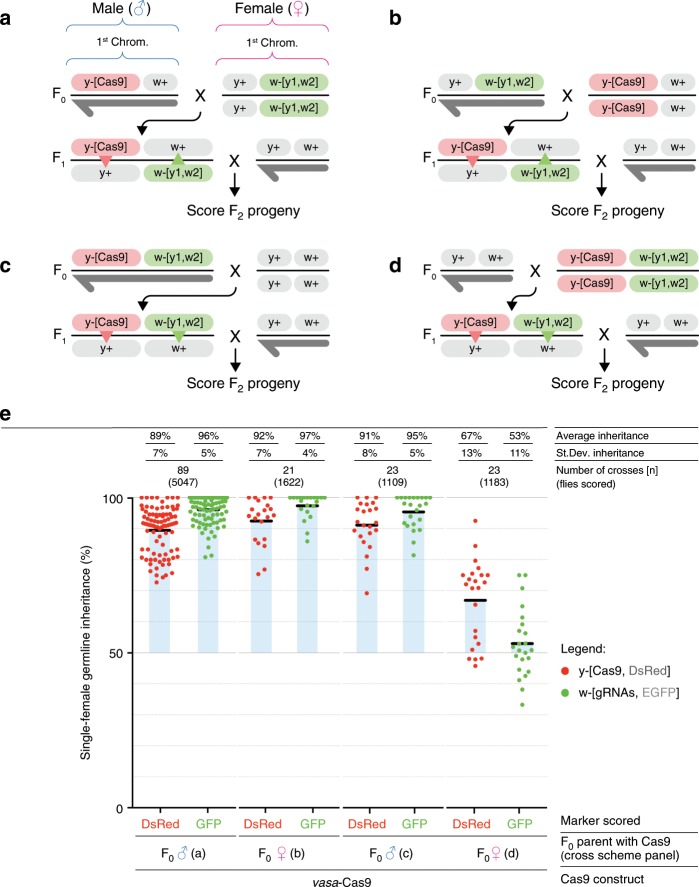
Fig. 2. tGD targeting the yellow and white loci uncovers the maternal effect mechanism.
a–d Genetic crosses performed using the tGD elements targeting yellow (DsRed-Cas9) and white (GFP-y1,w2-gRNAs) loci, both located on the first chromosome (X chromosome). Cross schemes used to test the F1 female germline by scoring the F2 progeny: a Cas9 from the F0 male and gRNAs from the F0 female, b Cas9 from the F0 female and gRNAs from the F0 male, c both Cas9 and gRNAs from the F0 male, and d both Cas9 and gRNAs from the F0 female. Allelic conversion events are indicated by the red and green triangles in the F1 females of every cross scheme. e Analysis of the F2 inheritance rates of the fluorescent markers for all cross scheme combinations (a–d) using Cas9 constructs driven by the vasa promoter. Strong super-Mendelian inheritance is seen for all conditions except when both Cas9 and the gRNAs are inherited from the F0 female (d). Values for the inheritance average (black bar), standard deviation, number of samples (n), and total number of flies scored in each experiment are represented over the graph in line with the respective data. Sex of the F0 parent carrying Cas9 is indicated with “♂” for males and “♀” for females in panel (e). Raw phenotypic scoring is provided as “Supplementary Data 2”.