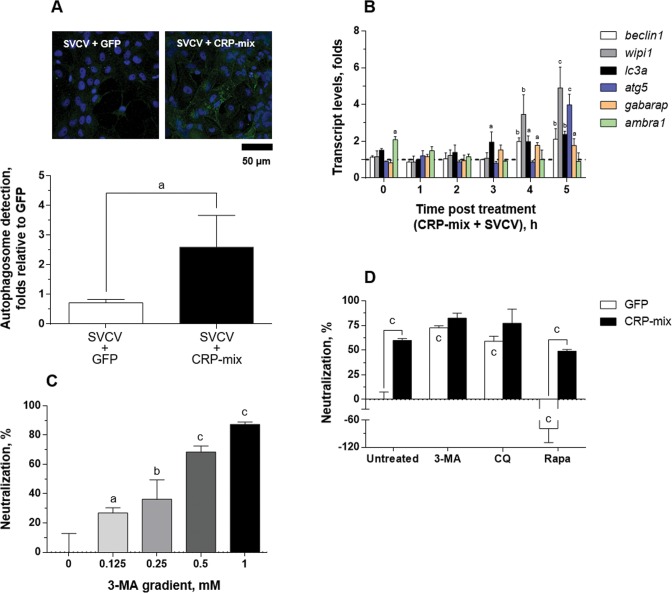
Figure 5.
Autophagy induced by CRP-mix on SVCV replication in the ZF4 cells. (A) Representative confocal images of the FITC immune-labelled LC3B in the ZF4 cells treated with either GFP or CRP-mix together with SVCV for 4 h. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Autophagosome levels were quantified as described in Fig. 4 and in the methods. The scale bar is equal to 50 µm. (B) Ability of the CRP-mix to modulate autophagy-related gene transcription in vitro during SVCV infection. The transcript levels of the genes of relevant autophagy elements (beclin1, wipi1, lc3a, atg5, gabarap and ambra1) were quantified by RT-qPCR in ZF4 cells treated with CRP-mix for 2 h before to viral inoculation (MOI of 1) at different times post adsorption (0–5 and 20 h). This experiment was performed twice in quadruplicate. The data are expressed as indicated in Fig. 3. (C) Effect of the autophagy blocker 3-MA on SVCV replication is shown. The SVCV neutralization activity of a gradient of 3-MA (0–1 mM) when incubated with EPC cells for 20 h prior to virus adsorption was assessed. SVCV infection was determined by the focus forming assay. The results are represented as the percentages of neutralization relative to the untreated group. (D) Effects of the CRP-mix on the SVCV neutralizing activity of autophagy modulators in vitro. SVCV infectivity was assessed on EPC cells treated with 3-MA (1 mM, 20 h), CQ (25 μM, 30 min) and rapamycin (Rapa, 25 μM, 4 h) and then incubated for 2 h with the CRP-mix before infection. SVCV infection was determined by the focus forming assay, and the data are presented as in (C) and relative to the GFP-treated group. Statistically significant differences in comparison to corresponding untreated groups and GFP are shown inside and on top of the bars, respectively. Neutralization experiments were performed 3 times each in triplicate. The statistically significant level differences are indicated with symbols as indicated in Fig. 1. Data were analysed by using one-way ANOVA (C) and two-way ANOVA (B,D) with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test and two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test (A).