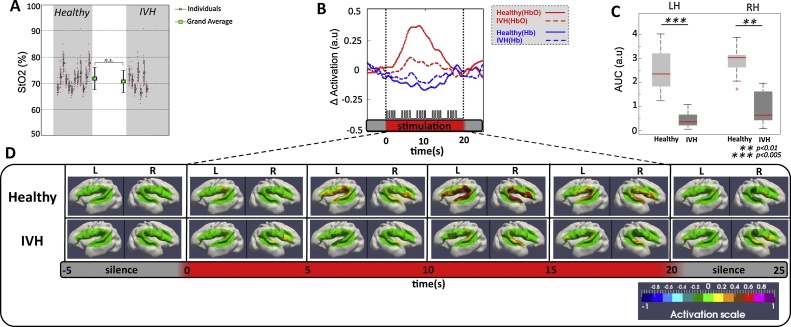
Fig. 3.
(A) Mean StO2 of Healthy (12 preterms) and IVH (7 preterms) infants during the experiment. Each thin black error bar indicates the mean and standard deviation across the 20 NIRS channels (red dots). Thick black error bars indicate mean and standard deviation of StO2 over Healthy and IVH preterm infants. (B) shows one sample fOI channel of grand-average of HbO (red lines), Hb (blue lines) changes for healthy (solid lines) and IVH (dotted lines) neonates during auditory stimulation. Horizontal red thick bars indicate the period of the stimulation (20 s). This response was pronounced for the healthy neonates, with a significant increase in HbO. (C) Comparison of the mean AUC changes of Oxy-Hb induced by auditory stimulation between healthy and IVH infants. For each hemisphere, activations were significantly reduced in the IVH group compared to the healthy group. (D) Topographies of the hemodynamic response in the two groups (Healthy, IVH). The HbO response, averaged each 5 s, was projected on a 3-D mesh of an individual 30 wGA preterm neonate. The red rectangle indicates the duration of auditory stimulation. The hemodynamic response in both hemispheres was weak in IVH neonates compared to healthy infants. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)