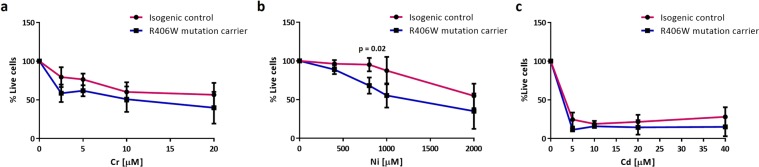
Figure 2.
Cr and Ni treatments in iPSC-derived iNeurons 30,000 iPSC from a R406W mutation carrier individual (F11362.1) and isogenic control line (F11362.1Δ1C11) were seeded in triplicate in 96 well plates and then differentiated into iNeurons for 3 weeks. After differentiation, iNeurons were treated with increasing doses of chromium (0–20 µM) (a), nickel (0–2000 µM) (b) and cadmium (0–40 µM) (c) for 72 hours and the (3‐(4,5‐dimethylthiazol‐2‐yl)‐2,5‐diphenyltetrazolium bromide) (MTT) assay was performed to assess the cell death induced by these three heavy metals. Results represent the percentage of live cells in treated iNeurons compared to untreated ones. Data shown are the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments for each heavy metal. Treatment with 800 µM Ni induced statistical significant cell death in R406W mutation carrier iNeurons compare with isogenic control (p-value < 0.05).